Reproduction of the article online. Micropropagation. Multiply text on a small example template
Reproduction of articles(multiplication of text) is a technology that allows you to get a large number of texts, unique from the point of view of search engines, from one article.
Copied texts are very cheap, but usually of extremely low quality. They are not created for users, but for search engines. Search engines quickly learned to identify such texts: the pages on which they are posted are poorly ranked or even drop out of the index. Today, the primitive automatic reproduction of articles is practically not used.
Goals
- Promotion of several (and more often - a large number) thematic resources;
- filling one site with the same type, but unique articles, descriptions (especially important when promoting online stores);
- posting on third-party resources of many thematic articles with links to your site;
- registration in catalogs, which requires a large number of unique names and descriptions of the same type of resource.
Technique
Reproduction of the text takes place in two stages:
- template preparation for reproduction;
- directly reproduction(generation) of texts.
Preparing the template
From the original article with special characters in a specific format, a document is created where synonyms are selected for individual words, phrases or sentences, and other individual words, phrases, sentences or even paragraphs are prepared for subsequent rearrangement. For example, the original text:
You need to reproduce articles carefully and competently.
Generation
The second stage uses special software... The program uses the template and generates the required number of text instances from it. For example, the pattern already familiar to us:
(Reproduce | Generate) (articles | texts) (necessary | necessary | should) and + ((very |) carefully | carefully | professionally) | competently.
Can give the following results:
It is necessary to generate articles accurately and competently. Reproduction of articles should be competently and very carefully. It is necessary to reproduce texts competently and carefully. etc.
The number of articles received depends on the length and quality of the template, as well as on the settings of the generator program.
Programs for reproduction of articles
Synonymizer
A program for the automatic selection of synonyms in the form required for subsequent generation. The synonymizer uses an internal synonym database, which can usually be updated and replenished.
The synonymizer does not know how to take into account the context and considers all synonyms to be completely equal. Sometimes this leads to the appearance of very funny expressions, for example, "ultrasonic scrubbing of the brow" (in the original "ultrasonic cleaning of the face").
At the present stage of development of PS algorithms, texts synonymized in a fully automatic mode are easily recognized by search engines, therefore, automatic synonymizing is not used today. Templates are also made entirely by hand.
Text generator
A program with functionality and various possibilities for generation. Often, generators already have a built-in synonymizer - to facilitate the work of the webmaster.
Article reproduction and SEO
Reproduction was an effective method and was used frequently around 10 years ago. In 2012-13, it was still of limited use. Now the PS requirements for the quality of content are such that the complexity and, as a consequence, the cost of reproduction is comparable to the cost of rewriting of acceptable quality. In such conditions, most webmasters and SEOs choose the services of web writers.
If you seriously decide to start promoting your site with the help of content, for which I personally use the exchange, then you should understand that it will not work to post links on other sites in only one article, since search engines will not take into account the link weight of a page with the same content.
For this, we have to make 1000 unique articles out of 1 article using the article multiplication method. special services or programs.
In order not to write many rewrites of one post, it will be easier to reproduce it and below I will show how this can be done in simple ways for a few minutes.
Reproduction of articles- this means making sure that 10, 20, 100 options are obtained from one article. In this case, the resulting text on the output must be unique.
I hope that you understand the importance of unique posts, and if not, then wait for the "" filter.
What is the essence of the method: you write one unique article and do several rewrites of each sentence, and also select several synonyms for all words. You pass the compiled template through the program, as a result of which the program will generate new articles, automatically replacing words with your rewrites of sentences and synonyms.
How to reproduce an article
1) First of all, we write a unique article. In order to check its uniqueness, there are a huge variety of services on the Internet that provide this service.
For me personally, it is much more convenient for me to use the program. I insert the article there and in the settings select those search engines in which you want to check it. I mark everything.

Then we press "Check uniqueness" and if your article has it from 90% or more, then everything is super, you can go to step 2.

2) Now download the program SEO-Anchor-Generator(link checked, no viruses found). With its help, we will reproduce future articles. Delete the template that is there by default and insert your text there.
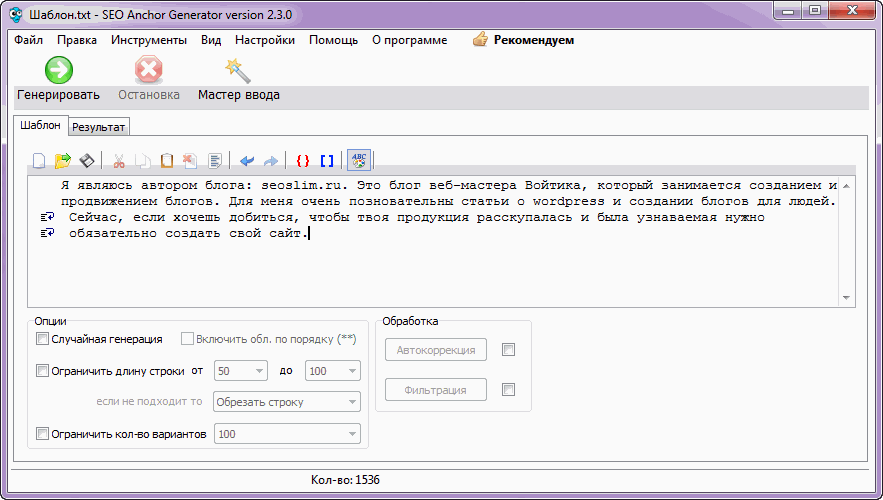
3) Now we will select synonyms for each word of the given text. The program works according to the following principle:
An example of my text template:I am the (author | creator | developer) of a blog.
As a result, the program will generate three sentences:
That is, the program takes words that are close in meaning from parentheses and substitutes them into new sentences. In order to write down synonyms, select the word and click "Input Wizard".

In this window, write synonyms for the selected word or phrase from a new line and press the "Insert" button.
The main thing is to choose such words as possible so that the meaning of the text does not change. The more synonyms you write, the more the program will be able to reproduce articles.
From my own experience, I was convinced that even two or three words are enough to get a lot of rewrites at the output.

As a result, we have all our synonyms enclosed in such brackets "()", and between themselves are separated by the sign "|" ... New articles will be generated from these words in brackets.
Click "Generate" so that the program starts to substitute words from "()" into new sentences.

See the result.

4) Now choose synonyms or phrases for each word in the text. This can take a very long time.
It even took me a whole day to reproduce one article, but believe me it's worth it, since search engines give more preference (they consider them more thematic and have more weight) links with surrounded by text. The more you can generate articles, the more you will get working links.
So in a few minutes, in a hurry, I redid my text:
After generation, I got a huge number of articles, but most of them are very similar to each other. Therefore, we press the button "Removing similar" and we filter out all the most repetitive articles.

But just in case, do not delete your template, otherwise it will suddenly come in handy.
That's all if it comes out a new version program or there will be another way to promote the site to the TOP, you will be the first to know about it if subscribe to update blog by email.
These programs will make life easier for the optimizer on the web. The first time will be difficult, and then it will be easier and easier. This is how you can simply copy the article. Good luck!
Reproduction of text by free software
Reproduction of the text today can be done free software... By functionality and a huge variety of interface. There is plenty to choose from for your needs and preferences. Some are provided with a synonym base, while others are not. Individual members of this family have the ability to supplement and edit. And even use several databases, create your own thematic ones. They also differ in the way they select unique articles. The simpler ones generate all the options with the calculation of the further selection of unique texts. Others immediately, during the reproduction of the text, discard inappropriate options. By controlling the syntax of the parentheses of the multiplication formula, one can select those that automatically check the correctness of the parentheses and those that assign it to the user. Basically, everyone uses two types of formulas: the formula for choosing one of the options and the formula for rearranging the options. The syntax of the first is the same for everyone. But according to the second, almost everyone uses their own version of the syntax. This must be taken into account if you are preparing a template for multiplying the text in one, and in the process of generating articles according to the formula, another will perform text multiplier... This point should also be taken into account by those who do not make a template for copying the text on their own, but order it from the performer.
Text reproduction with SEO Anchor Generator
This is the first program for reproduction of texts which I used in my work. Like the first programmable calculator, I will remember it forever. It should be noted that it is as simple and reliable as that very solid Soviet calculator. As the name suggests, it is designed to generate anchors. However, I, and not only me, used it to multiply the text. Thanks to the author for a reliable and simple tool that has served freelancers faithfully for many years.
Multiply Text with Article Clone Easy
 And this is the second "favorite". Already a more advanced option. I also used it in my work until I developed my own. There are quite a few possibilities in the ACE by the author. The most interesting moment is placement of links by anchors. No less interesting functionality is checking articles for uniqueness. And many thanks to this author. Many of his decisions pushed me to my own original options. The program includes: bases of Russian and English synonyms, a good instruction, a demo file.
And this is the second "favorite". Already a more advanced option. I also used it in my work until I developed my own. There are quite a few possibilities in the ACE by the author. The most interesting moment is placement of links by anchors. No less interesting functionality is checking articles for uniqueness. And many thanks to this author. Many of his decisions pushed me to my own original options. The program includes: bases of Russian and English synonyms, a good instruction, a demo file.
Generating The Web
 I'm not so familiar with this one. But there is some experience of use. I must say, a curious tool with its own useful features: external dictionaries, double check by the shingle method and much more.
I'm not so familiar with this one. But there is some experience of use. I must say, a curious tool with its own useful features: external dictionaries, double check by the shingle method and much more.
Reproduction of articles - why and how to do it?
If someone does not know, reproduction of texts(articles) is a technology with the help of which a lot is made from one text (articles) - dozens and even hundreds of different texts (articles) of the same content. The main difficulty of the process is to preserve the readability of all variants of the article and their uniqueness from the point of view of search engines with a minimum of human labor.
Why do you need to copy articles?
For the so-called article promotion ... At the moment, it is one of the most effective ways to promote your website in search engines. The method consists in placing thematic articles on third-party resources with links leading to the promoted site. Thus, the link mass is built up from the thematic pages of the site being promoted.
Since search engines do not include duplicate pages in the index base, all posted articles must be unique. Writing hundreds of articles by a copywriter is very expensive. Reproduction is two to three orders of magnitude cheaper and, moreover, is done much faster.
The need to reproduce texts may also arise when registering your site in hundreds of directories, which require many different descriptions of the site and its unique names. When buying a lot of links, you will also need to multiply the text of the anchor links and near-link text.
The cost of writing one article by a copywriter is 2-10 bucks per 1000 characters. And reproduction of an article to a thousand costs about 20 bucks for 1000 characters of the reproduced article. That is, the first way you can get a thousand articles (1000 characters each) for at least $ 2000, and the second way - for $ 20 Perceptible difference?
How is the copying of texts carried out?
First, the original article is prepared in a special way. With the help of special characters ((,), |, [,], etc.), all kinds of replacements and permutations of words, sentences and whole paragraphs are specified in it. Then, using a special program, - randomizer, - from this marked up source text, a set of texts is generated that are similar to each other, but unique from the point of view of search engines.
Suppose, for example, that you need to multiply the sentence: "Generation of texts from one source". We process this initial sentence:
(Generation (set | large number | hundreds | thousands |) | Reproduction) (texts | articles) from (one | only |) (source (text |) | source (article |))
We apply the randomizer,. His online demo tells us that it can generate 144 different texts from this text and give us a random 10 of them:
- Reproduction of articles from a single source
- Generation of a large number of texts from one source text
- Reproduction of texts from the source
- Generating articles from the original article
- Reproduction of texts from one source article
- Generation of hundreds of articles from a single source code
- Generating thousands of articles from source
- Generation of many articles from one source text
- Reproduction of texts from a single source
It is also necessary to select the most dissimilar from the generated options. This is usually done using the shingles method. If all this seems complicated to you, then you can order reproduction of articles by professional rewriters.
Of course, there are also problems. When copying texts, you always have to balance between their quality and quantity. The more articles are generated, the worse the readability of the text becomes and the percentage of coincidences of parts of the texts increases. To maintain readability, you have to limit yourself to fewer options.
17.03.2010
Last edit: 2010-11-28 04:44:35
Material tags:,
There are plants that will grow well in unpretentious environments - even indoors, even in the cold. By understanding which group the flower belongs to, it becomes reliable to determine the proper care. Most of the known plants are classified into classes. Others can be kept strictly on the street. Other species can be bred strictly at home without a natural setting. Critical components of cultivation consist of maintaining atmospheric moisture, timing the introduction of moisture into the soil, and controlling a safe temperature. The sun is one of the most important components.
Reproduction of indoor plants using microtechnology
The new biotechnology is called "clonal micropropagation". The term "micropropagation" refers to some methods of plant propagation in laboratory or artificial conditions. Simply put, the culture is propagated in vitro.
The method is based on the unique ability of each plant cell to give rise to a new plant. It is enough to take a tissue sample from certain parts of a plant - a mother plant (a plant with valuable traits that needs to be propagated) and place it under sterile conditions on a nutrient medium. From it, a microscopic plant will be obtained, which later develops into a normal shoot and which can be returned to the conditions of natural growth.
The method of clonal micropropagation of plants has a number of advantages over existing traditional methods of propagation.
The collection of rare and endemic plants collected in test tubes takes up much less space than traditional collections. In addition, labor costs for maintaining such a "bank" are lower than for annual field cultivation. Microcloning allows the preservation of thousands of specimens, preserving intraspecific diversity for the future.
 During reproduction, it is possible to use almost all parts of the plant: meristematic (growth, shoot-forming) parts of the plant (growth points, lateral buds, root tips, bases of young leaves, peduncles, etc. Bulb scales are well suited for bulbs, for roses and chrysanthemums - buds on the stem, for indoor decorative leafy begonias, Saintpaulias, gloxinia - parts of the leaf. You can even use parts of a flower. The size of the selected fragments is about 1 sq. cm. Then they are disinfected with special solutions and placed on a nutrient medium in test tubes or any other vessels the addition of various growth regulators Thus, at this stage, sterile "pieces" of the mother plant are placed on the nutrient medium in test tubes, and they begin to grow.
During reproduction, it is possible to use almost all parts of the plant: meristematic (growth, shoot-forming) parts of the plant (growth points, lateral buds, root tips, bases of young leaves, peduncles, etc. Bulb scales are well suited for bulbs, for roses and chrysanthemums - buds on the stem, for indoor decorative leafy begonias, Saintpaulias, gloxinia - parts of the leaf. You can even use parts of a flower. The size of the selected fragments is about 1 sq. cm. Then they are disinfected with special solutions and placed on a nutrient medium in test tubes or any other vessels the addition of various growth regulators Thus, at this stage, sterile "pieces" of the mother plant are placed on the nutrient medium in test tubes, and they begin to grow.
The term "clone" was proposed in 1903 by Webster (from the Greek klon - a stalk or shoot suitable for plant propagation. According to scientific terminology, cloning means obtaining identical organisms from single cells.
The first works in the field of clonal micropropagation were carried out in the late 1950s and are associated with the name of Georges Morel, who managed to obtain the first regenerant orchid plants. Cultivating under sterile conditions the tip of an orchid shoot, measuring only 0.5 mm, he observed the formation of spherical structures resembling modified buds. These structures could be divided, grown on an artificial nutrient medium, divided again and obtained from them whole plants. French orchid breeding firms used this method, and very soon mericlon orchids appeared on the flower market in huge numbers, transforming the orchid from an expensive and rare flower into a widespread plant.
The meristem method of plant propagation requires special approach to the organization of the process. This is the creation of sterile conditions and the availability of special equipment. Test tubes, flasks, scalpels and even table surfaces must be sterile. Expensive, but this is the only way to get the largest number of young shoots in the shortest possible time. The plant travels from the meristem to the "bed" in a few weeks.
 In laboratory conditions, the entire reproduction cycle is divided into four stages. First, tissue sections are taken from the shoot-forming areas of the plant. They are placed in test tubes with a liquid solution (hormones, vitamins, trace elements). Under such conditions, a piece of a leaf or root quickly "turns" into an independent plant with the rudiments of all vegetative organs. At the second stage, the future plant is transferred from a test tube into a flask with nutritive jelly. It has several compositions, which are often kept secret by experts. As soon as the roots and leaves have formed, it is time for the third stage. The shoot is again removed from the flask and the grown roots and leaves are cut off with a scalpel. They will be used for further breeding. The remaining "growth point" is placed in another flask of nutrient jelly. It will spend some more time there until it becomes a full-fledged plant.
In laboratory conditions, the entire reproduction cycle is divided into four stages. First, tissue sections are taken from the shoot-forming areas of the plant. They are placed in test tubes with a liquid solution (hormones, vitamins, trace elements). Under such conditions, a piece of a leaf or root quickly "turns" into an independent plant with the rudiments of all vegetative organs. At the second stage, the future plant is transferred from a test tube into a flask with nutritive jelly. It has several compositions, which are often kept secret by experts. As soon as the roots and leaves have formed, it is time for the third stage. The shoot is again removed from the flask and the grown roots and leaves are cut off with a scalpel. They will be used for further breeding. The remaining "growth point" is placed in another flask of nutrient jelly. It will spend some more time there until it becomes a full-fledged plant.
Flasks with shoots are stored in a separate room, in which all the necessary conditions... The main thing in this process is sterility. Test tubes, flasks, scalpels and even table surfaces ... Everything is thoroughly disinfected. The nutrient medium inside the flask is favorable for the growth of the fungus. If an infection occurs, all material is destroyed. Fourth - The final stage- a new plant is planted in a common cana, where it grows to the desired size. In such an intricate way, here, in a relatively short period of time, several dozen full-fledged copies are obtained from a small leaf or root.
This breeding technique can be practiced at home, which will allow you to get plants that reproduce with difficulty in other ways, as well as new varieties.
 To create a small micropropagation laboratory, you can use the simplest items, for example: a closed cabinet, equipped with lighting, heating and ventilation. It is desirable that it be made of metal, equipped with a lamp daylight(1000 - 1500 lux), installed in the upper part, a heating system (usually an electric panel makes it possible to maintain a temperature of 20-25C) and an aeration system (an electric fan is enough).
To create a small micropropagation laboratory, you can use the simplest items, for example: a closed cabinet, equipped with lighting, heating and ventilation. It is desirable that it be made of metal, equipped with a lamp daylight(1000 - 1500 lux), installed in the upper part, a heating system (usually an electric panel makes it possible to maintain a temperature of 20-25C) and an aeration system (an electric fan is enough).
You will need a sterilizer, disinfectant solutions, distilled water, and rubber gloves. A sterilizer is required to sterilize cutting instruments, containers and substrate. A commercially available disinfectant bleach (9-11% sodium hypochlorite) diluted in distilled water to 5% concentration is used to sterilize the work surface, after which it is rinsed with distilled water. A 1-2% solution is used to disinfect microscopes, which are then washed with distilled water. At all stages, work should be done with gloves.
Regular safety razor blades can be used to obtain microscopic cuttings of certain sizes; glass vessels with a wide neck are used as working containers. It is also recommended (although not necessary) to use a binocular microscope to help observe small micropropagated plants.
Substrates, growth promoters and special fertilizers The substrate commonly used for micropropagation is agar-agar - the best natural gelling agent obtained from red seaweed. Hormones and fertilizers are added to the substrate (nutrient medium). Pre-made media can be found in a wide range of drug stores or at companies selling chemicals for medical or pharmaceutical use. The resulting plants - seedlings are planted in peat soil with a pH of 5.5. Phytohormones of two types are used: for the proliferation of shoots and buds (for example, phytoquinine) and for rooting.
The first stage: the vessels are filled with a nutrient medium, enriching it with hormones. The blades and glass jars with the substrate are placed in a sterilizer with water and sterilized at a temperature of 110-120C for 20 minutes. At the same time, a working table is prepared by washing it with 5% sodium hypochlorite and distilled water. Then they take the very top of the plant that they are going to grow, choosing for a start simple plants, for example, Saintpaulia (if you have a microscope, it is placed on a stage), and the smallest leaves covering it are removed. Before placing this part of the plant in a vessel, it is disinfected with 1-2% sodium hypochlorite and washed with distilled water. The vessel is closed and placed in a cabinet, where it is kept for 20-40 days with lighting for 14 hours a day.
The second stage: when the microscopic cut grows up and appears as a green clot the size of a pea with the formed rudiment of organs, new containers are prepared by filling them with a substrate for rooting, and sterilized by placing them in a sterilizer along with cutting instruments. In the meantime, the vessel is taken out of the cabinet and the plants are removed from it, which are divided into parts with a blade. They are placed in new vessels, which are placed back in the cabinet, where they remain until the roots are formed (20-30 days), every day for 14 hours, turning on the light.
The final stage: when the plant has roots, they are removed from the vessels for micropropagation and planted in pots filled with very light humus (peat with a pH of 5.5). The pots are then placed in a protected environment (a small plastic pipe is sufficient) to allow the seedlings to gradually get used to their natural conditions. Once they have adapted (depending on the species after 4-6 weeks), the usual growing conditions for that species should be followed.
© 2007 Site materials are protected by copyright law. No material can be published without the written permission of the author. All rights belong to -Alexander Dovganyuk
Agroecology »Biotechnology» Clonal micropropagation of plants
Development of in vitro cultivation methods different types plants created the prerequisites for the application of fundamentally new approaches to their reproduction. At present, technologies for clonal micropropagation have been developed for a number of crops; method of vegetative propagation of plants based on in vitro culture. Such technologies are especially relevant for crops propagated in production mainly vegetatively (potatoes, fruit, berry, ornamental, forest plants). With prolonged vegetative propagation by traditional methods (cuttings, bulbs, whiskers, etc.) daughter plants accumulate viral, bacterial and fungal infection, which reduces the quality of the planting material. There is a need to improve the planting material from infection. Clonal micropropagation has the following goals:
1. Accelerated reproduction of unique genotypes in plant breeding;
2. Industrial propagation of high reproductive planting material in plant seed production;
3. Recovering the planting material from the viral. bacterial and fungal infections during reproduction;
4. Maintenance of non-constant material that is split during the process of seed reproduction (hybrids of fruit, berry, ornamental, and other crops)
5. Reproduction of crops with a long life of the whole (woody plants).
6. Reproduction of plants that are impossible or difficult to propagate in vivo (sterile forms for heterotic selection).
The advantages of clonal micropropagation over traditional methods are as follows:
1. The method provides a high multiplication factor. which makes it possible to quickly introduce new varieties of plants into production. The method has no alternative for species that are not propagated or difficult to reproduce in vivo;
2. In the process of reproduction, the planting material is improved by applying the methods of apical meristems, thermotherapy or chemotherapy;
3. A small amount of starting material, the ability to save it in genebanks, incl. in vitro;
4. Performing work in laboratory conditions, regardless of environmental conditions, saving space, the ability to regulate environmental factors;
5. The possibility of automation of in vitro cultivation, the use of industrial technologies for obtaining planting material.
The disadvantages of the method of clonal micropropagation include the complexity and high cost of the equipment used, the possibility of increasing the frequency of mutations in in vitro culture, and the rise in the cost of planting material. In this regard, clonal micropropagation is advisable to use to obtain high reproductions in seed production, followed by the use of traditional methods of vegetative propagation of healthy planting material.




