What are postal services? What services does Russian Post provide? Payment methods for postal services
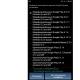
| Weight, g | Price
, without VAT |
| 20 | 110,00 |
| 40 | 113,00 |
| 60 | 116,00 |
| 80 | 119,00 |
| 100 | 122,00 |
* - fee for the declared value of a letter: for each full or incomplete 1 ruble of the estimated value is equal to 0.03 rubles.
** - SIMPLE notification RUB 22.92. without VAT
FAQ
Tariffs for services for forwarding notifications of delivery of internal registered postal items and postal transfers Money, effective from April 12, 2019.
- Simple notification- 22.92 rub.
- Registered notice- 56.67 rub.
- Electronic notification of delivery- 22.92 rub.
- Notifications of delivery of a postal transfer as part of the provision of the “Postal money transfer” service- 25.42 rub.
* When confirming payment for services with postage stamps, VAT is not charged
** The service also applies to RPO “1st Class Items”.
Letter- mail with a written message and (or) documents. Letters can be simple, registered or with declared value. Letters in postal envelopes measuring 114x162x5mm and 110x220x5mm and weighing up to 20 g are considered standard written correspondence. In internal simple and registered letters written messages and business papers are sent.
NOTE:
Tariffs for communication services DO NOT INCLUDE VAT. For communication services provided to enterprises and organizations, VAT is charged above the tariffs.
Good to know
In internal letters with a declared value, objects and documents are sent (securities, diplomas, passports, driver's licenses, pension and court cases, government bonds, shares, lottery tickets, civil registration certificates, diplomas, art cards, state postal marks payments, etc.) that represent a certain value to the user. It is prohibited to send Russian banknotes and foreign currency in letters.
Limit dimensions, weight:
- minimum size: 110x220mm or 114x162mm;
- maximum size: 229x324mm;
- weight limit: 100 g;
Russian Post is a very important company for the country. The state postal service performs many social functions. One of them is providing jobs, because more than 300,000 people work at the post office. This large team processes more than 1.5 billion letters, 75 million monetary units and 55 million parcels per year. In 2011, the enterprise's turnover amounted to more than 120 billion rubles, and net profit exceeded 790 million rubles. Russian Post was founded in 2002, and 11 years later the government included it in the list of strategic enterprises. The State Post provides a large number of services, the list of which increases every year.
Post services
- Written correspondence.
Written correspondence services are included in the universal services. Written correspondence includes:
Parcels,
Post cards,
Reply mail.
- First class shipments.
1st class items are quick way delivery. It allows you to speed up shipment by a third compared to traditional delivery. The main advantages of this service are:
Safety,
Low cost
Fast delivery.
Processing speed,
Convenience in determining tariffs.
When sending by cash on delivery, the parcel amount should not exceed 20,000 rubles. Delivery speed is ensured by new logistics and sorting technologies. For first class items, mailboxes are provided, the service of which is carried out much more often than the removal of correspondence from standard boxes.
First class mailbox
- Express deliveryEMS.
This service is provided in more than 190 countries. This allows parcels to be delivered to different parts of the world in the shortest possible time. The following types of express delivery are available:
Delivery within the city,
Intraregional delivery,
Delivery throughout Russia,
International delivery.
The weight of the parcel for express delivery should not exceed 31 kilograms. The length of the package should not be more than 150 centimeters.
- Courier delivery.
Recipients of parcels in Moscow have the opportunity to have the parcel delivered by courier from the branch directly to their door. This service can be ordered through mobile app Russian Post or SMS. The parcel is delivered within two days after completing the application. The cost of one shipment is 199 rubles. You must present an ID to receive it.
Russian Post application
- SMS notification.
This service involves notifying the recipient/sender of the arrival/receipt of mail. To order an SMS notification, do the following:
Specify the alert type,
Provide phone number
Fill out the order form,
Deposit money for the service.
Russian Post has determined the following tariffs for the provision of SMS notification services:
Prices include VAT.
- Multienvelope
The multienvelope is intended for sending the following goods:
Information carriers,
Souvenirs,
Plastic cards.
Advantages:
Delivery to any region of Russia;
The ability to use the service to promote your business (informing potential clients about promotions and discounts);
Stimulates seasonal sales;
Reasonable price for the service.
Restrictions:
Shipping abroad is not possible;
The multienvelope is manufactured industrially;
Not suitable for sending items weighing more than 150 grams;
Approval required appearance multi-envelope with Russian Post.
Tariffs for this service for a simple shipment they look like this:
| Weight | Price including VAT | Price excluding VAT |
|---|---|---|
| Up to 50 grams | 29.50 RUR | 25.00 RUR |
| 50–100 grams | 36.58 RUR | 31.00 RUR |
| 100–150 grams | 50.74 RUR | 43.00 RUR |
Tariffs for registered shipment:
| Weight | Price including VAT | Price excluding VAT |
|---|---|---|
| Up to 50 grams | 63.72 RUR | 54.00 RUR |
| 50–100 grams | 77.88 RUR | 66.00 RUR |
| 100–150 grams | 94.40 RUR | 80.00 RUR |
VAT is not charged if payment is confirmed by government signs (postage stamps).
Financial services
- Payment of pensions.
This service is one of the most socially significant. For decades, the Russian postal service has been paying pensions and benefits to citizens. Pension Fund and Russian Post jointly developed an electronic document management system that allows pensioners to be notified in a timely manner about the amount and timing of payments. More than 17 million pensioners use state postal services.
- Acceptance of utility payments.
The convenience of this service lies in the fact that Russian Post has many branches throughout the country. Therefore, citizens have the opportunity to choose the nearest branch to their home so as not to waste a lot of time on the road. State Post is constantly improving the quality of customer service. The post office cooperates not only with municipal utility providers, but also with federal-level companies, for example, Gazprom OJSC.
- Money transfers.
- Accepting payments for Internet and television.
- Insurance services.
- Service bank cards.
- Issuance and repayment of loans.
Russian Post does not stand still. State postal service employees are constantly introducing new services for their customers. In 2015, new financial services of Russian Post appeared, aimed at improving the quality of service in the field of insurance, money transfers and parcel delivery.
Services for the population
Russian Post provides not only postal and financial services. State Post strives to help its customers solve everyday issues. Among the most popular Russian Post services for the population are the following:
- CyberPress,
- CyberMail,
- subscription to printed publications,
- mobile app,
- sale of lottery tickets,
- sale of tickets for transport, public events, etc.,
- telephone communications,
- acceptance of migration papers.
Russian Post provides a very wide range of services. Almost every resident Russian Federation can choose for himself those services that are suitable and useful for him. Criticism of the state postal service regarding the timing and quality of delivery has its grounds. But Russian Post offers various express delivery options, which are more expensive than regular delivery, but provide significant guarantees. The following offers for business are also provided: advertising, partnership, customs support, assistance with international shipments. It is thanks to its social orientation that Russian Post is such an important organization for the state.
Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Posted on http://allbest.ru
Characteristics of the facility's services postal service
Types of services provided by postal organizations
Postal service organizations (objects) provide users with universal, contractual and Additional services postal services, carry out other activities permitted by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Postal services- activities related to the reception, processing, transportation, delivery (handing over) of postal items, as well as the implementation of postal money transfers.
Universal postal services- postal services to meet the needs of users in the exchange of written correspondence by affordable prices on the territory of the Russian Federation.
Additional services- services provided by postal operators for an additional fee: writing a written message and address on a postal item, postal order form; filling out notifications of delivery of postal items and postal orders; packaging of postal items; storage and home delivery of letters and parcels with declared value, postal orders, parcels, etc.
Negotiatedpostal services- services provided by postal facilities on a contractual basis (reception, processing, transportation and delivery of parcels, postal containers, as well as items Email; distribution of printed publications, delivery and payment of pensions, benefits and other payments intended purpose; provision of telephone conversations and services for receiving and transmitting telegraph messages; sale of securities; acceptance, forwarding and payment of postal orders; reception and collection of cash proceeds; accepting payments for utilities, etc.).
Postal services are provided by postal operators on a contractual basis.
Under an agreement for the provision of postal services, the postal operator undertakes, on the instructions of the sender, to forward the mail entrusted to him or to carry out a postal transfer of funds to the address specified by the sender and deliver (hand over) them to the addressee. The user of postal services is obliged to pay for the services provided to him.
Postal operators are obliged to ensure the forwarding of written correspondence to users of postal services within the specified time frame. Standards for the frequency of collecting written correspondence from mailboxes, standards for its exchange, transportation and delivery, as well as target dates for its forwarding are developed by the federal executive body that manages activities in the field of postal services, and are approved by the Government of the Russian Federation.
The terms for the provision of other postal services are established by postal operators independently.
Postal operators are obliged to provide users of postal services with information about the established deadlines for the provision of postal services, as well as about delivery standards approved by the Government of the Russian Federation and target deadlines for sending written correspondence.
Internal mail, internal postal transfer- postal item, postal order accepted for forwarding and delivery to the addressee on the territory of the Russian Federation.
Postal category- a set of characteristics that determine the procedure and conditions for acceptance, processing, transportation and delivery (delivery) of postal items (simple, registered, declared value, ordinary).
Domestic mail and postal orders include the following types of mail:
· parcels (simple, custom, with declared value);
· secograms (simple, customized) - written messages and publications with raised font for the blind, submitted openly, and cliches with secograph signs, as well as sound recordings and special paper intended for the blind, if they are sent by an organization for the blind or addressed to such an organization. ;
· postal transfers (simple, expedited);
· direct containers (ordinary, with declared value);
· domestic express mail;
· sending emails.
Postal transfers, depending on the method of delivery, are divided into:
· simple postal transfers- sent using the postal network;
· expedited postal transfers- sent using electrical communication networks - telegraph, electronic, etc.
For individual senders and addressees, the following categories of postal items and postal orders are established: government, military and official.
Government mail- postal items sent by persons determined by the Rules for the provision of postal services.
Military mail and postal orders- postal items and postal orders sent and received by military units and institutions, as well as their personnel.
Service mail and postal transfers- postal items of postal operators and simple postal orders from organizations (objects) of the federal postal service.
Limit weight and dimensions of domestic mail items
For domestic mail, the following dimensions and weight limits are established:
Table1 .
|
Type of departure |
Weight limit (kg) |
Packed size |
|
|
110*220 mm; 114*162 mm; 162*229 mm; 229*324 mm; 250*353 mm |
|||
|
postcard |
|||
|
Parcel mail including one book attachment (stitched folder) |
Maximum: 36 cm in one of three dimensions (length, width, thickness), the sum of the three dimensions should not exceed 70 cm. For rolled parcels - 70 cm in length and 15 cm in diameter. In some cases, parcels rolled into a tube can be accepted up to 150 cm in length, when the attachment cannot be folded (maps, diagrams, etc.); Minimum: 105*148 mm, for rolled parcels - 10.5 cm in length and 5 cm in diameter |
||
|
Maximum: 50*50*40 cm. Separate parcels with objects up to 200 cm in length are accepted, provided that the perimeter of the largest cross-section does not exceed 150 cm; minimum (except for parcels with bees): 105 x 148 mm (with a minimum thickness of 50 mm). One side of a parcel with bees sent by air must be at least 30 cm. |
1. Letters in postal envelopes measuring 114*162*5 mm and 110*220*5 mm and weighing up to 20g are classified as standard written correspondence.
2. Parcels, one of the sides of which exceeds the dimensions of 50*50*40 cm, are classified as large-sized.
3. Parcels weighing over 10 kg are classified as ponderous. Reception and delivery of heavy parcels weighing up to 20 kg are carried out at postal facilities specially designated for this by postal organizations.
4. Parcels weighing up to 3 kg, the largest side of which does not exceed 36 cm, and the sum of three dimensions does not exceed 70 cm, are classified as small.
International mail- postal items accepted for forwarding outside the Russian Federation, arriving on its territory from a foreign state or in transit.
International postal items include the following types of items:
· letters (simple, registered, with declared value);
· postcards (simple, registered);
· parcels and bags "M" (plain, custom);
· secograms (simple, custom);
· small packages (custom);
· parcels (ordinary, with declared value);
· international shipments express mail;
· sending emails;
· grouped shipments "Consignment".
Postal items of diplomatic and consular missions of foreign states, international intergovernmental organizations and representative offices of foreign states at these organizations in the Russian Federation for forwarding within the Russian Federation, as well as postal items addressed to these institutions are paid for and registered as internal, but are processed, forwarded and delivered to the procedure provided for international postal items.
Simple letters weighing up to 20 grams and postal cards sent to employees of Russian institutions abroad (embassies, consulates, representative offices of international organizations, etc.) are paid for and processed as domestic mail, but are processed and sent in the manner prescribed for international mail. .
International postal items are accepted for shipment to countries with which postal exchange is established.
Letters with declared value, small packages and parcels are accepted for shipment only to the countries listed in the Guidelines for the Acceptance of International Postal Items, which is compiled on the basis of information from the International Bureau of the Universal Postal Union and is put into effect by order of the federal executive body that manages activities in the field postal service.
Limit weight and dimensions of international postal items
For outgoing international mail, the following dimensions and weight limits are established:
Table 2.
|
Type of departure |
Weight limit (kg) |
Packed size |
|
|
maximum: 229*324 mm; minimum: 110*220 mm or 114*162 mm |
|||
|
postcard |
|||
|
Parcel |
maximum: the sum of length, width and thickness - no more than 90 cm; greatest dimension- 60 cm. For rolls, the sum of the length and double diameter is no more than 104 cm; largest dimension - 90 cm; minimum: 105*148 mm. For rolls, the sum of length and double diameter is no more than 17 cm; largest dimension - 10 cm |
||
|
Small package |
Maximum: the sum of length, width and thickness - no more than 90 cm; the largest dimension is 60 cm. For rolls, the sum of the length and double diameter is no more than 104 cm; largest dimension - 90 cm; minimum: 105*148 mm. For rolls, the sum of length and double diameter is no more than 17 cm; largest dimension - 10 cm |
||
|
any dimension - no more than 105 cm. The sum of the length and perimeter of the largest cross section - no more than 200 cm; minimum: 110*220 mm or 114*162 mm |
Payment methods for postal services
Payment for postal services is charged when accepting postal items and postal orders at the rates in effect on the date of acceptance.
Payment for postal services, with the exception of universal postal services, is determined according to tariffs established on a contractual basis.
Payment for universal postal services is determined on the basis of tariffs approved by the federal executive body for regulating natural monopolies in the field of public postal services in the manner established by the Government of the Russian Federation.
Postal services are paid for with state postage stamps, in cash circulating on the territory of the Russian Federation, or by non-cash payments.
State postage signs- postage stamps and other signs applied to postal items and confirming payment for postal services. forwarding written postal correspondence
Marked envelope (marked card)- a standard postal envelope (postcard), issued by the federal executive body that manages activities in the field of postal services, with a typographic image on it of a postage stamp and the emblem of federal postal organizations.
State postal payment marks are used to pay for the sending of written correspondence, simple and registered notifications of delivery of postal items and payment of postal orders.
It is the responsibility of the sender to affix stamps to written correspondence in accordance with the approved rates for its forwarding.
As state postal payment marks, postage stamps are used, affixed to postal items or printed on postal envelopes and postal cards (postal packages), imprints of state postal payment marks applied by franking machines, as well as other marks applied by printing, established by the federal body. executive power, managing activities in the field of postal services, and confirming payment for postal services.
State postage signs indicate the name of the state in Russian "Russia" and in Latin transliteration "Rossija", the amount of payment in Arabic numerals or with Latin letters, year of manufacture or registration number. In addition, they may contain the word “Mail” written in Russian or Latin letters. The fee amount may be replaced by a note indicating that payment has been made in full.
Franking machine- a machine designed for applying state postal payment marks to written correspondence, confirming payment for postal services, the date of receipt of this correspondence and other information.
The procedure for using franking machines and state postal payment marks applied by printing is established by the federal executive body that manages activities in the field of postal services.
The issuance of permits for the use of franking machines on the territory of the Russian Federation is carried out by the federal executive body that manages activities in the field of postal services. Requirements for franking machines approved for use on the territory of the Russian Federation are agreed upon by the manufacturer and (or) his official representative with the specified federal executive authority.
Franking machines are registered in accordance with the established procedure in the organization (at the facility) of the federal postal service.
Uncanceled postage stamps cut from marked envelopes and postcards can be used to pay for the sending of letters, parcels and postcards within the Russian Federation.
Other cut-out government postage signs are not used to pay for postage.
If the dimensions of the postal item do not allow it to be stamped with a franking machine cliche, then the imprint can be made on a separate sheet of paper, which is then pasted onto the postal item.
Persons guilty of manufacturing for the purpose of marketing or selling knowingly counterfeit government postal payment marks shall bear liability in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
State postal payment marks are placed in the upper right corner of the postal envelope, postal package, postcard, parcel. It is prohibited to stick postage stamps one on top of the other. The stamps are canceled with a calendar stamp so that they cannot be reused.
When canceling postage stamps, the correct payment for postage is checked.
Sold government postage stamps will not be accepted back or exchanged. Postage stamps withdrawn from postal circulation, damaged (dirty, damaged, sealed, canceled in any way), as well as foreign postage stamps are not used to pay for sending domestic and international written correspondence.
International reply coupons issued by the International Bureau of the Universal Postal Union are accepted as payment for international letter correspondence. They are printed on paper with watermarks depicting the abbreviation “UPU” in large print and, as a rule, have on the front side an imprint of the calendar stamp of the foreign postal organization that sold the coupon.
International response coupon- a security issued by the International Bureau of the Universal Postal Union, subject to exchange for government postage stamps.
International response coupons presented when submitting a postal item are exchanged for stamps in accordance with the payment rate for one simple international letter weighing up to 20 grams sent by air.
Persons guilty of manufacturing for marketing purposes or selling knowingly counterfeit international response coupons are liable in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Delivery of letters (parcels) with declared value and postal orders addressed to citizens at home is paid by either the sender or the addressee.
Unpaid or incompletely paid letters, postcards and parcels placed in mailboxes are not sent to their intended destination, but are returned without cancellation of stamps to the senders for full payment.
In the absence of the sender's address, the specified unpaid or incompletely paid international mail items are transferred to the number of undelivered items, and domestic mail items are forwarded to their destination and issued to the addressee after receiving additional payment from him at the established rates. If the addressee refuses the additional payment, such mail items are transferred for temporary storage to the number of unclaimed items.
Determination of fees for sending postal items and postal orders
The fee for sending postal items depends on the type and category of postal item, its weight, and the amount of declared value. For insured parcels and parcels, in addition, the postage fee depends on the distance over which the postal items are sent and on the method of sending them.
The fee for sending postal transfers depends on the amount of the transfer and the method of sending it.
Postal service quality indicators
Quality of postal service. The inseparability of the process of providing postal services from the process of its consumption places high demands on the quality of postal services. Even minor omissions in the work of one employee, site, workshop, facility or postal service organization can cause irreparable damage to the user of postal services. To assess the quality of postal services, the following indicators are used: quality of user service and quality of postal services
The quality of user service is characterized by the density of the network of postal facilities, their operating modes, waiting time and user service, additional services when providing postal services.
The density of the network of postal facilities is determined by the standards for the placement of postal service centers and postal service points, as well as the standards for the placement of mailboxes for collecting written correspondence.
The operating hours of postal facilities are established taking into account ensuring maximum convenience for users of postal services. The operating mode of postal facilities included in the structure of the Federal State Unitary Enterprise "Russian Post" is established depending on the class assigned to the object.
The waiting time and user service are determined by the number of operating windows, the availability of modern technical means and technologies, the qualifications of workers and the speed of service. The shorter the waiting time in line and the shorter the time spent by the employee on receiving mail, the higher the quality of service.
Additional service (work, services) when providing postal services is not a mandatory element of the work of licensees and is carried out subject to availability technical capabilities. For example, a postal worker can, at the request of the user and for a fee, apply the necessary inscriptions to the envelope of the postal item, pack it, fill out accompanying forms, etc.
The quality of postal services is characterized by the speed of passage of postal items, the stability and regularity of postal messages, the safety of postal items and funds, and complaints about the quality of postal services.
The speed of postal items is determined by control deadlines and standards.
The control period is understood as the maximum time within which the transportation of postal items and postal orders, their processing and delivery (delivery) must be ensured. Control periods, depending on their purpose, are divided into general, stage-by-stage and intraoperative.
General control periods characterize the time it takes for a postal item or postal order to travel from the sender to the addressee.
Phased control dates characterize the time standards for performing individual operations of the production process within one postal facility.
Intraoperative control periods characterize the time standards for completion individual elements, which together constitute a specific production operation.
Control deadlines for sending postal items and postal orders refer to general control deadlines. Control deadlines for sending written correspondence are developed and approved by the Ministry of Communications of Russia. Control deadlines for sending insurance and parcel mail are developed and approved by the Federal State Unitary Enterprise of Russia.
Control deadlines for sending written correspondence and parcel mail are tables indicating vertically and horizontally the names of cities that are the administrative centers of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation. At the intersection of the horizontal row and the vertical column is the desired target date. In table 5.1. the control period (5 days) for sending written correspondence from Arkhangelsk to Barnaul is shown. The control period does not include the day of receipt of the postal item.
Tables with control deadlines for sending written correspondence and parcel mail must be located in each postal facility.
The deadline for sending written correspondence on the intracity territory of federal cities and administrative centers of constituent entities of the Russian Federation is 2 days.
The deadline for sending written correspondence between the administrative centers of municipal districts on the territory of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation is 2 days.
The deadline for sending written correspondence between the administrative center of a municipal district and settlements located on the territory of the municipal district is 3 days.
The deadline for sending written correspondence between settlements included in different municipal districts of the Russian Federation is calculated by summing up the corresponding deadlines.
The quality of sending postal items or postal money transfers is considered satisfactory provided that at least 90% of their total quantity is completed within the target time frame.
The following standards have been established for written correspondence.
1. Standards for the frequency of collection of written correspondence from mailboxes.
From mailboxes located outside postal facilities:
* on the intracity territory of cities of federal significance, on the territory of administrative centers of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation - 5 days a week at least twice a day, on the remaining two days - at least once a day;
From mailboxes located inside postal facilities - on weekdays at least once a day.
2. Standards for the frequency of exchange of written correspondence between postal facilities are established in accordance with the frequency of delivery of written correspondence to these postal facilities.
3. The standard for the frequency of transportation of written correspondence between federal cities, administrative centers of constituent entities of the Russian Federation, administrative centers of municipal districts, and other settlements is at least 3 days a week at least once a day.
4. Standards for the frequency of delivery of written correspondence:
* on the intracity territory of cities of federal significance, on the territory of administrative centers of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation - daily at least once a day;
* on the territory of administrative centers of municipal districts - at least 5 days a week at least once a day;
* on the territory of other settlements - at least 3 days a week, once a day.
Reducing the frequency or stopping the collection from mailboxes, exchange, transportation and delivery of written correspondence is possible only during emergencies of a natural or man-made nature based on decisions of Rossvyaz adopted in accordance with the Regulations on priority use, as well as suspension or limitation of the use of any communication networks and means of communication during emergencies of a natural or man-made nature, approved by decree of the Government of the Russian Federation.
The stability and regularity of postal messages is characterized by the implementation of schedules and timetables for the movement of postal transport on postal routes.
Appeals with complaints about the quality of postal services are accepted at postal facilities. In accordance with the Rules for the provision of postal services, the procedure for registration and consideration of claims of users of postal services is established. To consider claims, an internal audit is carried out, and the applicants are informed about its results.
The number of claims received is one of the main indicators of the quality of work of a particular postal facility, formed directly by users of postal services.
Records of incoming requests must be kept as a whole for each licensee, as well as for each of its branches and separate structural units. It is recommended that all incoming requests, depending on the reasons for their occurrence, be divided into to the following groups:
* claims related to non-receipt of postal items and postal money transfers;
* claims related to theft or damage to mail attachments;
* claims related to unsatisfactory user service in postal facilities;
* claims related to the long passage of postal items and postal money transfers;
* claims related to other reasons.
When analyzing received requests, the most common violations of the rights and legitimate interests of users are determined, the reasons for their occurrence are identified, and measures are developed to eliminate them.
Quality control of postal services. Quality control of postal services is carried out at all stages of the passage of postal items and postal orders. The main ways to control the quality of postal services are: production control, operational control, mutual control, control of delivery deadlines, documentary checks and surprise checks of the state of cash registers, control through the clientele, control through an independent audit, control of licensed activities.
Production control is carried out at each postal facility and is intended to detect and eliminate defects in work before dispatch from the facility. Production control is carried out by the heads of postal facilities, their deputies, heads of structural divisions and other employees at the direction of the facility managers in a continuous or selective manner in parallel with the processing of postal items.
The frequency of control and inspection standards are established by special instructions of the licensee. The results of control are reflected in a special journal for each workplace and are used to identify and eliminate deficiencies in work and eliminate the causes of defects.
Operational control is carried out directly by postal workers in the form of control operations, which are component operations of production processes for receiving, processing and sending mail. Defects in work are detected and eliminated directly at the workplace.
Mutual control of postal facilities consists in the fact that defects in work are detected not in the object where it was admitted, but in another. This marriage can no longer be eliminated.
The postal facility that discovered the defect reports this with an act f. 51 or notice f. 30 to the postal facility that committed the defect. Act f. 51 is drawn up in the event of violations entailing financial liability.
If violations are detected that do not entail financial liability, a notice f. 30. Such control includes control of the correct execution of postal items, postal orders and postal documentation, carried out by post offices subordinate to the OPS.
Control of transit times allows you to identify defects that remained undetected during the passage of a postal item or postal money transfer, based on the discrepancy between the actual transit times and the normative ones. One of the control methods is the distribution of control letters by the territorial bodies of Rossvyaznadzor.
Documentary checks and surprise checks of the state of cash registers include checking the safety of all material assets and funds, the correctness of production documentation, and compliance with financial and technological discipline. Scheduled checks and surprise audits of cash registers are carried out. The procedure for conducting such checks is specified in special instructions FSUE Russian Post.
Control through the clientele makes it possible to detect defects that remained unopened during processing in postal facilities. A user who has received a postal item in violation of the delivery deadlines, damaged or not received it at all, contacts the postal service facility with a corresponding claim, which is confirmation of a defect in the work of the postal service organization. In addition, one of the ways to communicate with users is to send control letters objects of postal service, which allow us to establish not only negative, but also positive sides operation of postal facilities.
Control through an independent audit allows you to obtain an assessment of the quality of postal services provided through the implementation of control measures public organizations or associations, specialized organizations or associations, specialized quality audit companies. The methodology for carrying out such an audit can be very different: surveys of the population and business entities, government bodies and municipalities, testing of services, test purchases, etc.
State supervision of activities in the field of communications (control of licensed activities) is carried out by the territorial bodies of Rossvyaznadzor in accordance with the Procedure for the implementation of state supervision of activities in the field of communications, approved by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation. All licensees are subject to verification.
There are scheduled and unscheduled inspections. The territorial bodies of Rossvyaznadzor carry out scheduled inspections to supervise activities in the field of postal services in accordance with their annual and quarterly plans. Each licensee must be inspected at least once every two years. Unscheduled inspections are carried out at the request of licensees, based on customer complaints about the quality of services, and if a result of remote control, i.e. without direct interaction with the licensee, significant violations in the work of the licensee. Based on the results of state supervision, inspection reports are drawn up, which indicate the identified violations mandatory requirements in the field of postal services, or a note is made about the absence of such violations.
State supervision of activities in the field of postal services includes supervision and control over compliance by licensees with mandatory requirements and norms established by regulatory legal acts in the field of postal services, as well as control over compliance with the legislation of the Russian Federation on licensing in the field of communications.
Supervision and control over compliance with mandatory requirements and norms in the field of postal services includes the organization and implementation of inspections:
* compliance with the requirements for the construction of postal networks, requirements for the design, construction, reconstruction and operation of postal networks (structures);
* compliance by postal operators with the rules for the provision of postal services;
* compliance with metrological requirements for equipment used to record the volume of postal services provided;
* compliance with standards for the frequency of collection from mailboxes, exchange, transportation, and delivery of written correspondence;
* compliance with deadlines for sending postal items and postal money transfers;
* compliance with the procedure for recording transmitted and received postal items and funds between postal organizations.
* Enforce the use of franking machines and identify franking machines that are not authorized for use.
Monitoring compliance with the legislation of the Russian Federation on licensing in the field of communications includes inspections:
* compliance with the license conditions established in licenses to carry out activities in the field of providing postal services (hereinafter - license terms);
* identifying persons engaged in the provision of postal services for a fee without the appropriate licenses.
The procedure for organizing and conducting measures to monitor the activities of licensees in the provision of postal services is defined in the relevant methodology. The methodology is developed and approved by the Russian Ministry of Communications and undergoes state registration with the Russian Ministry of Justice.
Control measures are carried out through direct interaction with the postal service object being inspected or through remote control. Documentation is checked, postal items and postal money transfer forms are inspected.
Document verification is carried out selectively for the last six months preceding the verification. If, during selective control, the identified number of postal items (documents) with violations is less than 10%, then the state inspector of the Russian Federation for supervision of communications will make a decision on compliance with the requirements in the field of postal communications.
If, during selective control, the identified number of mail items (documents) with violations is more than 10%, then the state inspector draws up an order that lists the identified violations and indicates the time frame for their elimination. If violations are detected or if violations identified during previous inspections are not eliminated, the state inspector draws up a protocol on the administrative violation.
The procedure for considering a case of an administrative offense is carried out in accordance with the Code of the Russian Federation on Administrative Offenses. Depending on the identified administrative offenses. Depending on the administrative violation identified, the protocols are sent to the courts or reviewed by senior government inspectors.
The senior state inspector (ex officio or heads of territorial bodies of Rossvyaznadzor and their deputies) based on the results of the consideration of the case makes a decision on bringing to administrative responsibility.
Ways to improve the quality of postal services
Improving the quality of postal services involves reducing the delivery time of postal items and postal money transfers, increasing the level of their safety, providing users with access to information about the real quality of the services offered, taking into account the assessment of independent experts.
The main areas of work to improve the quality of postal services are:
* implementation of international quality standards;
* improving postal logistics;
* automation and mechanization of postal processing processes;
* introduction of new technologies - automated systems control (track and trance systems) using modern infocommunication technologies;
* increasing production and technological discipline of postal workers;
* introduction of new types of postal packaging that have increased security against unauthorized opening.
International quality standards are developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). The purpose of these standards is to ensure a sustainable improvement in the quality of services provided or products produced. The international standard ISO 9001:2008 (GOST R ISO 9001-2008) is in force in the Russian Federation. If the requirements established in the standards are strictly observed, the services provided will always have a quality that satisfies users.
The ideology of building standards is based on 8 principles:
1) focus on the user of services;
2) the desire for leadership in their field of activity;
3) involving employees in the quality improvement process;
4) process approach to solving assigned problems;
5) a systematic approach to solving assigned problems;
6) the desire for continuous improvement;
7) making decisions based on reliable information;
8) mutually beneficial cooperation with suppliers of services and goods.
The presence of a voluntary ISO certificate is for the user a sign of the quality of the services provided, an additional guarantee of reliability and evidence of professional competence. Work on voluntary certification is carried out in three stages: preliminary estimate, verification and assessment of the quality system in the organization, inspection control over the certified quality system.
On preparatory stage a preliminary external audit is carried out to assess the quality management system in force in the organization to identify problem areas. At the second stage, based on the results of the preliminary audit, a program of measures is developed to eliminate the identified inconsistencies with the requirements of international standards.
After the implementation of the program, the quality system in the organization is checked and assessed for compliance with the requirements of international quality standards. If the assessment is positive, a corresponding certificate is issued for a certain period. The third stage consists of inspection control (at least once a year) during the validity period of the certificate in order to confirm compliance of the organization’s quality system with the requirements of the GOST R ISO 9001-2001 standard.
Improvement of postal logistics is carried out on an ongoing basis, taking into account ongoing changes in the country's transport system. At the same time, logistics is understood as a direction in the economy within which the problem of developing and implementing an integrated system for managing material and information flows is solved. Changes to mail routing plans are made as necessary, but at least once a year, in order to speed up mail transportation by reducing the length of postal routes, choosing the fastest mode of transport, and reducing the number of transit stages of mail processing.
The introduction of new technologies should include automation and mechanization of postal processing processes. Postal processing equipment, developed on the basis of new information and communication technologies, in combination with barcoding, allows you to increase the speed of processing postal items and reduce the number of errors during sorting.
The use of a bar code generated at the stage of receiving registered mail contributes to the implementation of automated control systems (“track and trance” systems).
These systems, based on Internet technologies, allow the recipient of services to receive information in real time at what stage of delivery the postal item is at and when it was delivered.
Strict adherence to production and technological discipline by postal workers is a necessary condition compliance with postal processing standards, ensures the safety of postal items at all stages of shipment.
New types of postal packaging (reusable polymer boxes for written correspondence, secure polymer bags) contribute to the transition from traditional sealing using sealing wax, lead seals and twine to new sealing methods.
Polymer seals and holographic stickers used today do not require additional mechanisms, are applied manually and are easily destroyed when trying to hide a postal item (postal item) under mechanical or thermal influence. New sealing methods make it possible to simplify, and therefore speed up, the external inspection procedure and identify signs of unauthorized opening.
conclusions
The Russian Postal Service provides customers with universal, contractual and additional services. Domestic and international postal items and postal orders are sent through the postal network.
Domestic postal items include: postcards, letters, parcels, parcels, secograms, direct containers, domestic express mail, e-mail items. In addition, postal orders are sent in internal exchange.
International postal items include: letters, postcards, parcels and “M” bags, secograms, small packages, parcels, international express mail items, e-mail items, grouped “Consignment” items.
Each item has characteristics that determine the procedure and conditions for receiving, processing and delivering this postal item. The combination of these characteristics is the category of postal item.
For domestic mail and postal transfers, the following categories are established: government, military, service. For domestic and international postal items, the maximum weight and dimensions are determined, which are specified in the Rules for the provision of postal services. Postal services are paid according to tariffs. The fee for sending postal items depends on the type, category, weight of the item, and the amount of assessment of the postal item.
The fee for sending parcels and parcels with declared value also depends on the distance over which they are sent. The fee for sending a transfer depends on the transfer amount and the transfer method. Postal services are paid for using postage stamps, in cash, or by bank transfer.
Posted on Allbest.ru
Similar documents
The essence, types and rules for processing postal items. Rules for the provision of postal services. The procedure for receiving and delivering domestic registered mail. Analysis and features of the turnover of postal correspondence with declared value.
course work, added 07/28/2010
The placement procedure and principle of development of the postal network, its central facility and services offered. Features of the work and advantages of a mobile post office, its importance in providing services to residents of remote villages in modern Russia.
course work, added 05/06/2010
Postal items, postal money orders to be delivered to your home and issued at postal facilities. Delivery of postal items by postman to your place of residence. The procedure for receiving outgoing domestic parcels and adding them to the invoice.
test, added 05/23/2010
The procedure for placing and the principle of development of a network of post offices and mailboxes in the city. Calculation of the number of post offices open type. Organization of customer service with postal services and design of mail transportation.
course work, added 02/07/2011
Economic and geographical characteristics of the Amginsky ulus. Placement of a network of enterprises and communication points. System for building intra-district postal communications and organizing mail transportation. Delivery of correspondence and printing. Indicators of planned activities.
course work, added 11/05/2014
Methods of organizing security systems, their characteristics. Access control and registration system. Equipment for safe storage values. Security check of the Omsk post office. Protection of classified information and equipment.
thesis, added 05/14/2015
The structure of the system of regulatory documents in the field of use of postal services. Terms in regulatory documents and definitions of their concepts. Problems of eliminating existing contradictions in terminology. Convention and Agreement of the Universal Postal Union.
test, added 01/25/2009
Organization of work and automation of postal operations using software products: “Tracking system”, “Retail newspapers”, “Subscription”. Organization of mail delivery at communication centers. The procedure for sending excess cash balances to post offices.
course work, added 03/28/2013
Express Mail Service (EMS) as a service for express delivery of items. Rules for filling out the address form and sending express items. Delivery of express items EMS, forms of payment. Filing claims and applications to search for EMS express shipments.
thesis, added 06/01/2010
The procedure for placing and the principle of development of a network of post offices and mailboxes in the city. Systems for processing and promoting mail in the city. Organization of mail transportation in the city. Organization of mail delivery in the city. Organization of city service mail
Service list
Post services;
services for the population;
Financial services;
services for legal entities.
Post services
The company's postal services are most widespread. Here you can send letters, parcels, and written correspondence. For special cases, express delivery is provided, as well as a 1st class system. In order to always be aware of the location of the parcel, the client can activate a special SMS notification service.
Financial services
All kinds of financial services are also equally popular. These include, first of all, Money transfers, opening deposits, insurance services, paying loans, servicing credit cards, issuing microloans, servicing bank cards. In addition, at the Post Office you can receive benefits, a pension, pay for utilities, as well as services for using the Internet, television and telephone communications.
Subscription to newspapers and magazines
Russian Post is notable for providing special services to the population, such as subscribing to magazines and newspapers, selling lottery tickets, postcards, and holding special promotions. The company accepts migration notifications and sends documents to universities.
Services for legal entities
For legal entities, Russian Post is ready to provide special services for customs clearance, as well as international mail.
The company provides advertising, postal and financial services for business owners. In particular, it carries out money transfers, places printed advertisements in its branches, and also distributes information and promotional materials to the addresses of the population.