Which processor to choose for a gaming computer. Which processor to choose. Gaming Computer Motherboards
To connect the computer processor to the motherboard, special sockets are used. With each new version processors received more and more features and functions, so usually each generation used a new socket. This negated compatibility, but made it possible to implement the necessary functionality.
Over the past few years, the situation has changed a little, and a list has emerged Intel sockets, which are actively used and supported by new processors. In this article we have collected the most popular sockets Intel processors 2017, which are still supported.
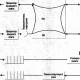
Before we look at processor sockets, let's try to understand what they are. A socket is the physical interface connecting the processor to the motherboard. The LGA socket consists of a series of pins that align with the plates on the underside of the processor.
New processors usually need a different set of pins, which means a new socket. However, in some cases, processors remain compatible with previous ones. The socket is located on the motherboard and cannot be upgraded without completely replacing the board. This means that upgrading the processor may require a complete rebuild of the computer. Therefore, it is important to know which socket is used on your system and what you can do with it.
1. LGA 1151
LGA 1151 is the latest Intel socket. It was released in 2015 for the Intel Skylake generation of processors. These processors used the 14 nanometer process technology. Since the new Kaby Lake processors haven't changed much, this socket is still relevant. The socket is supported by the following motherboards: H110, B150, Q150, Q170, H170 and Z170. The release of Kaby Lake brought the following boards: B250, Q250, H270, Q270, Z270.
Compared with previous version LGA 1150, USB 3.0 support has appeared here, the operation of DDR4 and DIMM memory modules has been optimized, and SATA 3.0 support has been added. DDR3 compatibility was still maintained. For video, DVI, HDMI and DisplayPort are supported by default, while VGA support can be added by manufacturers.
LGA 1151 chips only support GPU overclocking. If you want to overclock the processor or memory, you will have to choose a higher-end chipset. In addition, it was added Intel support Active Management, Trusted Execution, VT-D and Vpro.
In tests, Skylake processors show better results than Sandy Bridge, and the new Kaby Lake is even several percent faster.
Here are the processors that run on this socket on this moment:
SkyLake:
- Pentium - G4400, G4500, G4520;
- Core i3 - 6100, 6100T, 6300, 6300T, 6320;
- Core i5 - 6400, 6500, 6600, 6600K;
- Core i7 - 6700, 6700K.
Kaby Lake:
- Core i7 7700K, 7700, 7700T
- Core i5 7600K, 7600, 7600T, 7500, 7500T, 7400, 7400T;
- Core i3 7350K, 7320, 7300, 7300T, 7100, 7100T, 7101E, 7101TE;
- Pentium: G4620, G4600, G4600T, G4560, G4560T;
- Celeron G3950, G3930, G3930T.
2. LGA 1150

The LGA 1150 socket was developed for the previous fourth generation of Intel Haswell processors in 2013. It is also supported by some fifth-generation chips. This socket works with the following motherboards: H81, B85, Q85, Q87, H87 and Z87. The first three processors can be considered entry-level devices: they do not support any advanced Intel capabilities.
The last two boards added support for SATA Express, as well as Thunderbolt technology. Compatible processors:
Broadwell:
- Core i5 - 5675C;
- Core i7 - 5775C;
Haswell Refresh
- Celeron - G1840, G1840T, G1850;
- Pentium - G3240, G3240T, G3250, G3250T, G3258, G3260, G3260T, G3440, G3440T, G3450, G3450T, G3460, G3460T, G3470;
- Core i3 - 4150, 4150T, 4160, 4160T, 4170, 4170T, 4350, 4350T, 4360, 4360T, 4370, 4370T;
- Core i5 - 4460, 4460S, 4460T, 4590, 4590S, 4590T, 4690, 4690K, 4690S, 4690T;
- Core i7 - 4785T, 4790, 4790K, 4790S, 4790T;
- Celeron - G1820, G1820T, G1830;
- Pentium - G3220, G3220T, G3420, G3420T, G3430;
- Core i3 - 4130, 4130T, 4330, 4330T, 4340;
- Core i5 - 4430, 4430S, 4440, 4440S, 4570, 4570, 4570R, 4570S, 4570T, 4670, 4670K, 4670R, 4670S, 4670T;
- Core i7 - 4765T, 4770, 4770K, 4770S, 4770R, 4770T, 4771;
3. LGA 1155

This is the oldest supported socket on the list for Intel processors. It was released in 2011 for the second generation Intel Core. Most Sandy Bridge architecture processors run on it.
The LGA 1155 socket has been used for two generations of processors in a row, and is also compatible with Ivy Bridge chips. This means that it was possible to upgrade without changing the motherboard, just like now with Kaby Lake.
This socket is supported by twelve motherboards. The senior line includes B65, H61, Q67, H67, P67 and Z68. All of them were released along with the release of Sandy Bridge. The launch of Ivy Bridge brought the B75, Q75, Q77, H77, Z75 and Z77. All boards have the same socket, but some features are disabled on budget devices.
Supported processors:
Ivy Bridge
- Celeron - G1610, G1610T, G1620, G1620T, G1630;
- Pentium - G2010, G2020, G2020T, G2030, G2030T, G2100T, G2120, G2120T, G2130, G2140;
- Core i3 - 3210, 3220, 3220T, 3225, 3240, 3240T, 3245, 3250, 3250T;
- Core i5 - 3330, 3330S, 3335S, 3340, 3340S, 3450, 3450S, 3470, 3470S, 3470T, 3475S, 3550, 3550P, 3550S, 3570, 3570K, 3570S, ;
- Core i7 - 3770, 3770K, 3770S, 3770T;
Sandy Bridge
- Celeron - G440, G460, G465, G470, G530, G530T, G540, G540T, G550, G550T, G555;
- Pentium - G620, G620T, G622, G630, G630T, G632, G640, G640T, G645, G645T, G840, G850, G860, G860T, G870;
- Core i3 - 2100, 2100T, 2102, 2105, 2120, 2120T, 2125, 2130;
- Core i5 - 2300, 2310, 2320, 2380P, 2390T, 2400, 2400S, 2405S, 2450P, 2500, 2500K, 2500S, 2500T, 2550K;
- Core i7 - 2600, 2600K, 2600S, 2700K.
4. LGA 2011

The LGA 2011 socket was released in 2011 after LGA 1155 as a socket for high-end Sandy Bridge-E/EP and Ivy Bridge E/EP processors. The socket is designed for six-core processors and all Xenon processors. For home users, the X79 motherboard will be relevant. All other boards are designed for enterprise users and Xenon processors.
In tests, Sandy Bridge-E and Ivy Bridge-E processors show pretty good results: performance is 10-15% higher.
Supported processors:
- Haswell-E Core i7 - 5820K, 5930K, 5960X;
- Ivy Bridge-E Core i7 - 4820K, 4930K, 4960X;
- Sandy Bridge-E Core i7 - 3820, 3930K, 3960X, 3970X.
These were all modern intel processor sockets.
5. LGA 775

It was used to install Intel Pentium 4, Intel Core 2 Duo, Intel Core 2 Quad and many others processors, up to the release of LGA 1366. Such systems are outdated and use the old DDR2 memory standard.
6. LGA 1156

The LGA 1156 socket was released for the new line of processors in 2008. It was supported by the following motherboards: H55, P55, H57 and Q57. New processor models for this socket have not been released for a long time.
Supported processors:
Westmere (Clarkdale)
- Celeron - G1101;
- Pentium - G6950, G6951, G6960;
- Core i3 - 530, 540, 550, 560;
- Core i5 - 650, 655K, 660, 661, 670, 680.
Nehalem (Lynnfield)
- Core i5 - 750, 750S, 760;
- Core i7 - 860, 860S, 870, 870K, 870S, 875K, 880.
7. LGA 1366

LGA 1366 is a version of 1566 for high-end processors. Supported motherboard X58. Supported processors:
Westmere (Gulftown)
- Core i7 - 970, 980;
- Core i7 Extreme - 980X, 990X.
Nehalem (Bloomfield)
- Core i7 - 920, 930, 940, 950, 960;
- Core i7 Extreme - 965, 975.
conclusions
In this article, we looked at generations of Intel sockets that were used before and are actively used in modern processors. Some of them are compatible with new models, while others are completely forgotten, but are still found on users’ computers.
Latest Intel socket 1151, supported by Skylake and KabyLake processors. We can assume that the CoffeLake processors that will be released this summer will also use this socket. There used to be other types of Intel sockets, but they are already very rare.
 Hello everyone Let's talk about Intel hardware, or rather about which socket is best to build a computer on in 2016 or 2017, although now it is still 2016, I think that this information will easily be suitable for 2017. So I’ll write everything in simple words and these guys are exactly my opinion, my thoughts and all that
Hello everyone Let's talk about Intel hardware, or rather about which socket is best to build a computer on in 2016 or 2017, although now it is still 2016, I think that this information will easily be suitable for 2017. So I’ll write everything in simple words and these guys are exactly my opinion, my thoughts and all that
So now it’s 2016, the 775th socket is long gone, so we won’t talk about it, although guys, this socket still haunts fans..
So I’ll start with the 1366th socket, this is also an old socket, but it would be stupid not to write about it. The fact is that the 1366 socket was positioned as a solution for very powerful computers, so even today this socket carries many modern games. Socket 1366 supports a three-channel memory mode, there are i7 processors with 6 cores for this socket, but since they come with Hyper-Threading technology, that is, with threads, Windows sees such a percentage as 12-core. By the way, the processors are made using a 45 nm process technology. Even today, the 1366 socket is powerful, if you have a top-end i7, maximum Opera, a normal video card, then, as I already wrote, many games will run on such hardware. Speaking of opera, according to some sources, socket 1366 supports a maximum of 24 gigabytes of DDR3, according to other sources, 48 gigabytes. But it seems that you can install 48 gigabytes on the X58 chipset. In general, this topic needs to be studied, I think that 48 gigs can still be installed, I myself have read some reviews and, so to speak, there is no smoke without fire... Well, you understand...
I also wanted to say about the 1366 socket that, of course, everything is cool there, well, I’m talking about six-core i7s, but the only joke guys is that they will already lag behind modern models in terms of performance. In short, I mean that a six-core i7 on a 1366 socket is an old processor and therefore it will be slower than modern four-core processors, not by much, but slower, and at the same time it will consume more energy..
By the way, the most powerful processor on 1366 socket, do you know which one? This is the i7 990X model, really cool, here is a screenshot of the CPU-Z program with this percentage:

But the 1366 socket has one more big plus: there are motherboards on this socket that support working with two processors at once. That is, as I wrote, such power is hardly needed by an ordinary user. Here is an example of a motherboard on which you can install two processors:

By the way, this is the ASUS Z8PE D12X model
And I’ll write something else to you, so if you suddenly look for a motherboard for socket 1366, then be careful! The funny thing is that there are new motherboards for 1366 socket, some are new, but they are NONEAME, and this name is CHINESE. I strongly do not recommend such motherboards!
So what else do we have there? There is a 1155 socket, I don’t have much to say here, because it is almost the same as the 1150 socket, but less productive. This socket is newer than 1366, but I still don’t recommend it, because it’s already outdated hardware, not today, not tomorrow... The 1155 socket supports 32 gigs of DDR3 opera, quad-core i7s that come with threads. But again, in principle you can buy it if it’s at a good price, but once again, the 1155 socket will be about 20 percent slower than the 1150 socket, well, about that much
Here are the processors on the 1155th socket, I don’t know if this is the whole list, but there are definitely some popular ones here (those with the letter K are overclockable):

Let's move on, now we have 1150 socket. Well, what can I say, in principle this is a modern socket, but I don’t recommend it either and I’ll write why. This means that the 1150 socket is the same 32 gigabytes of DDR3, the same quad-core processors, but if on the 1155th socket they are made using a 32 nm process technology, then on the 1150th socket it is already 22 nm, this is a plus (the processors are a little faster and cooler) . In general, everything is fine with this socket, it is almost the same as the 1155, but a little faster.
But why don’t I recommend taking even the 1150 socket, although it seems to be modern? And because 1151 sockets have already been released, here it is, this is exactly what I advise you to take both in 2016, although it is already ending, and in the beginning of 2017. 1151 sockets have the same price as 1150, but are more powerful, there is a newer generation of processors and DDR4 support, in general there are serious advantages, and the price is the same. In general, I still consider the 1151 socket platform to be the best in terms of price and performance, believe me, it’s true. DDR4 support will allow you to build up a really large amount of RAM over time; you can cram all 64 gigs, versus 32 gigs on the 1150 socket. And top models of processors on socket 1151, this is really cool guys, because it’s very powerful
Look, these are just cool processors on socket 1151, just a note for you, look:

Why are they suddenly cool? But because they are on the coolest Kaby Lake core!!!
In principle, this is all that can be considered. There are also platforms 2011/2011-3, as I understand it, this is a continuation of socket 1366 and ordinary users are unlikely to need these platforms, they are very expensive and very powerful. For games this is super powerful, it’s simply not needed, believe me. And the prices there are simply outrageous...
So, what else is there on the sockets? Well, there is also socket 775, which I mentioned at the beginning. I think you are familiar with him, but maybe you don’t. In short, guys, this is an old socket. Yes, it’s really old, but is it worth burying it? I think it’s not worth it, everything happens in life and if you want to know what the 775th socket is capable of in 2017, then I will answer you, it is not capable of anything. And it will be a joke of course! The 775 socket is good in the sense that it’s not so dead, you can take a Q9650, overclock it, install a standard video card, 16 gigs of opera, and in principle I think you can play something...
There's another thing here, it's the price. A kit for used top-end hardware on the 775 socket will not cost that little guys. If you throw in a couple more tens of bucks, you can get the newest budget hardware on socket 1151, yes it will be budget, but the prospect of an upgrade is great. And don’t forget that between the 775th socket and the 1151st socket the difference is like an abyss, that is, very big. There, on socket 1151, the Pentium may already be even faster than the stock Q9650, I mean this seriously, after all, technology does not stand still.
So, what conclusion will we draw? I think we will. The best socket for 2016/2017 is definitely the 1151st, both in terms of price and performance. Believe me that this is the case, although you will probably still check this information, but I’ll tell you this, I won’t lie to you. You can take 1150, but 1151 is still better. Socket 1366 is for amateurs who want power and not cost too much, although finding boards on the 1366 socket is not an easy task. The 775th socket is even more for amateurs; it’s already difficult to squeeze anything out there even taking into account the overclocking of the Q9650. But for an office computer, the Q9650 will still be enough for a long time. The 1155th socket is also sufficient for an office, even if there is some kind of tree stump.
I completely forgot, there is also socket 1156, but this is generally a rare beast, I don’t know why. It’s older than 1155, and it’s clear that I don’t recommend it either. But it was on it that there was such a frame as a dual-core i5, which had 2 cores and 4 threads, by the way this is the i5 661 model, and maybe there were other models, I don’t know for sure, but on socket 1155 and the following sockets there is no such confusion anymore
In general, these are the things guys, it’s best to take 1151 socket, we’ll finish here, it seems that everything that is needed is what I wrote. And if I didn’t write something, then you’ll have to forgive me. Good luck to you and may everything go well for you
25.12.2016A lot of years have passed since a company called VIA disappeared from the consumer electronic market. Since then, the list of companies producing processors used in desktop PCs has consisted of only two main brands: the company AMD and company Intel. However, due to the fact that each company has a wide variety model range, it is quite difficult to choose a processor that will be the optimal solution for the tasks at hand.
First of all, you need to understand that high level Nuclearity and increased frequency are not evidence of processor power. The main criterion is compliance with the modern level of architectural solutions.
The design of modern processors

Taking into account their design features, processors are usually divided into three types:
Central. These processors belong to the category of classic ones. They carry computing cores, the number of which can vary from 2 to 10, built-in cache memory, and a RAM controller.
Having a graphite accelerator– the most numerous type, in which this graphic element plays the role of a fairly cheap discrete video card.
Single-chip systems– represent a 100% autonomous solution. So much so that they don't even need the presence of a motherboard chipset to interact with both systems sound devices, and network, and of course with computer memory and various storage devices.
The cornerstone of AMD and Intel processors for PCs is considered to be the x86_64 architecture. It implies compatibility with operating systems such as MacOS, BSD, Windows and Linux. Whereas for the construction of Qualcomm and Mediatek ( mobile processors) is used Alternative option ARM architecture, for IBM - POWER, and for Fujitsu - SPARC. Performance increases slightly each time, relative to the previous one, when a new implementation is carried out in the x86_64 architecture.
Intel processor series

Celeron J, Celeron N, Pentium J and Pentium N– a list of processors belonging to the line of processors considered to be the lowest of all produced by Intel. They don't even go into implementation individually. They are usually included in the package for budget motherboards. To build models bearing the J index, the somewhat outdated Bay Trail architecture is used, while the N index indicates the most modern Braswell architecture. If you compare the performance indicators between the computing cores produced by Braswell and those released by Bay Trai, they will be approximately the same. And this is despite the fact that the speed of integrated graphics in the latest chips has been increased by 3 or even 4 times. The Celeron J/N model is dual-core, and the Pentium J/N is quad-core. These processors are mainly used in super-cheap office computers, which are designed for web surfing and processing documents received in the form of electronic files.
Celeron G and Pentium G– processors with two cores, however, the performance level of each of the cores on the older Haswell and Skylake architectures is significantly higher than that of the aforementioned Bay Trail and Braswell. Their differences lie in the frequency and size of the memory cache. These characteristics are of course important for the processor, but they are not the most important. Taking into account the fairly low cost, it is most practical to use these processors in computers intended for home use, used for surfing the Internet, watching movies and basic games. Whereas the requirements of the most sophisticated games can no longer be satisfied by the capabilities of two cores.
Core i3 and Core i5 are either pseudo quad-core or true quad-core Intel processors. From a physical point of view, the Core i3 has only two cores, but the use of Hyper-Threading technology allows each core to process data in two threads. For this reason operating system and applications Core i3 is defined as an ordinary quad-core. Naturally, the performance of four virtual Core i3 cores is 1.5 times less than that of the physical four Core i5 cores, which also have support for automatic overclocking Turbo Boost. From which we can conclude that for games paired with a video card up to GeForce GTX 980, it is quite possible to get by with a Core i3. At the same time, Core i5 is more suitable in tandem with video cards of the new NVIDIA 1000 series. In addition, it is used for professional software, such as a video editor.
Xeon and Core i7– respectively, the working and senior consumer lines of Intel processors. Core i7 chips for LGA1151 and LGA1150 motherboards have four physical and eight virtual cores. And models with the K index can be overclocked manually, but provided that a motherboard with an Intel Z87, Z97 or Z170 chipset is used. Only with the help Core processors i7 has the opportunity to unleash the potential of the flagship GeForce GTX 1080 video card. True, it is possible to use a combination of two simpler video cards instead. Xeon chips, whose purpose is to be used in workstations, are an advantageous alternative to Core i7. They have a lower frequency, but their cost is lower. True, it can’t be called for games the best option, although it is quite suitable for video editing. However, while Xeon LGA1150 processors can use regular consumer motherboards, Xeon LGA1151 require a board with a special working Intel C232 or C236 chipset.
Core i7 Extreme Edition- are included in the number flagship models not only from Intel, but also in the market as a whole. The Core i7 is intended to be used by hardcore gamers and computer enthusiasts in their computers. The family includes models with from 6 to 10 physical cores and from 12 to 20 virtual threads. For older models you will have to pay over $1,500, and this does not even take into account the cost of the LGA2011-v3 motherboard, which costs at least $250.
AMD processor series

Sempron and Athlon– two- and four-core processors from AMD, which do not have much power, but are quite cheap. AMD AM1 chips are sold separately, since they are not soldered into the motherboard. This means that the kit, which includes the motherboard and processor, will cost, if not cheaper, then at the same price as Intel. But at the same time, it will be possible to more accurately select the equipment of ports and connectors for a specific task. Significant disadvantages of AM1 include the presence of a noisy box cooler fan, and this significantly narrows its scope of application.
A4, A6, A8, A10 and Athlon II X4 (FM2+) is a mid-level AMD platform. The main focus in it was on the balance between integrated graphics and the performance of computing cores. Particularly noteworthy are the A8 and Athlon II X4, which are among the most affordable quad-core processors suitable for gaming. A8 processors have powerful integrated graphics, comparable to a discrete graphics card GeForce GT 730. Athlon II X4 does not have integrated graphics, but their price is 2 times lower than the Intel Core i3. We can say that FM2+ can well be used in the process of assembling a gaming PC, however, provided that it is used if it is at the entry level
FX-4000, 6000, 8000 and 9000 (AM3+)– AMD’s older platform, which can no longer be called young. Its presence on the market for 5 years significantly affected the cost, which decreased significantly. This is what caused her to remain popular. The main negative feature of FX processors is the presence of an outdated 32-nm process technology, which provokes increased requirements for power supply and cooling system. Simply put, you will have to purchase a fairly reliable motherboard and a more massive processor cooler. However, all these costs are covered due to the fact that they themselves are inexpensive. AMD processors FX, so you will have to spend no more than $110.0 to purchase a six-core one, and an eight-core one will cost only $130.
Is it worth replacing the old processor with a new one?

The problem is not only in installing a computer from scratch, because you also have to think about the need to upgrade an already worn-out system. However, each new integration of Intel's Core architecture allows on average no more than a 5% increase in performance, and therefore the difference between the current processor and the one released 5 years ago will be about 25%. And here it’s worth thinking about whether it’s worth purchasing new processor also be spent on purchasing a motherboard with a new connector and RAM DDR4.
Those who have to assemble a computer should understand that the socket is one of the key concepts. Most novice users, when they need to replace parts, begin to wonder which socket to choose? You can understand this issue only when you know exactly what it is and why it is needed.
Correct selection of motherboard
It is strictly forbidden to install powerful components on a cheap motherboard. It will not be able to function at full capacity and withstand heavy loads. Likewise, a weak processor does not require a powerful motherboard, since the money will be wasted.
It’s better to start selecting a motherboard after the rest of the components have been purchased. Only after this can you decide on the class of the motherboard and the type of connectors.
So, socket is a type of motherboard connector that corresponds to the connectors in the processor. Highlight:
- sockets starting with the letters AM, S, FM – to support AMD processor
- sockets with the letter combination LGA, installed in Intel processors

You can find out which socket is suitable for your processor by reading the instructions. As a rule, the method of choosing a motherboard means purchasing it at the same time as the processor.
It should be noted the number of sockets in the motherboard. If you need to assemble a server, it is better to purchase a motherboard with several socket connectors. Processor support depends on their number. If the board has two sockets, it can interact with 2 processors at once. The maximum number of sockets on one board is four.
Modern motherboards and sockets
The majority of motherboards are produced by AMD or Intel. However, the sockets for them are not interchangeable analogues for each other.

For all Intel brand processors they make boards with sockets
- LGA 1150 (Socket 1150 model)
- LGA 1155 (Socket 1155)
- LGA 2011 (Socket 2011 model)
Previously, the manufacturer Intel developed models LGA 1156 or 1366. Older versions of the processor use LGA 775 and PGA 478. The numbers in the name reflect the number of contacts. The processor has a certain number of legs or pads.

AMD creates sockets of a different type for processors. Now the new version is considered to be socket FM1, FM2, FM2+. In addition, you can also buy the AM3+ model. Motherboards with sockets designated AM3, AM2, AM2+ are considered more outdated. At the same time, the “plus” indicates that the socket is compatible with the updated version of the processor. Models 754 and 939 are called obsolete, but despite this, they can be found today in offices and personal devices.
We hope that now you will learn to understand not only the concept of socket itself, but also some of its subtleties.