Adaptive layout code. Adaptive layout: what it is and how to use it. Adaptive layout - where to start
In order for the layout of your site to look good on iPhone or tablets, it must be adapted to these devices and it is important to do it efficiently...
Adaptive website layout (sometimes also called mobile-friendly) - DETAILED and step by step as in the lesson:
Please note: Yandex and Google have their own tools with which you can check the site for adaptability. Yandex has new version For webmasters, it is located like this: tools - checking mobile pages.
If you want to know how to make a responsive website design, then this will be written below and in detail in the examples, BUT, if you do not have skills in working with css, it will be more difficult. Or your programmer or webmaster can do this.
Responsive website design - involves setting the width of the page window and the width of columns and sidebars in %, in adaptive - in px.
Please note: if you have a popular engine for your site, such as wordpress, then they do not have a “headache” with adaptive design - everything is done there in a couple of mouse clicks - the plugin is simply installed and activated and that’s ALL). For example, for WP - I used WPtouch - it is very good, but if you have a full-time programmer, then it is better to do this moment individually.
You need to understand that basically, with adaptive layout, the following are often manipulated: width (width of the element: max-width and min-width), float (wrapping, it is removed as the width of the window decreases), font-size (the height of the letters is changed).
1) First you need to write a special meta tag for different types devices:
2) Adaptive page parameters (width and height):
Container (
width: 800px
max-width: 90%;
}
In this case, a fixed container width is set, but it should not be more than 90% of the window width, and this is very convenient - then the site itself will adapt to the size of the window.
3) Css adaptive layout for images of the entire site:
img (max-width: 100%;
height: auto;
}
Here we show that the size of the picture: its maximum width should be no more than 100% of the eye - this way the picture itself adjusts to the size of the phone or other gadget. Here is such a simple method - adaptive image design.
4) Adaptive layout of website text: in this case, manipulations occur with font height: font-size and other parameters.
Break-word ( word-wrap: break-word; )
This CSS is designed for hyphenation when there are long non-hyphenated words.
There are many errors in font size: Yandex loves to write - Text size is too small to read on mobile devices ah - for this we do this:
body (font-size: 16px) - this will avoid this error, and for the p tag and for links you need to put it separately. It is precisely because the body tag contains font-size: 12 or 14 px that this error occurs! And this is the verdict:
5) Adapting a 3-column design or 2-column layout - there is nothing complicated about this if everything is done on divs - oh, then usually you need to cancel the wrapping, that is, set float to none and the blocks will go down.
6) Adaptive CSS for video (from Habr):
Video (
position: relative;
padding-bottom: 56.25% ;
height: 0 ;
overflow: hidden;
) .video iframe ,
.video object
.video embed (
position: absolute;
top: 0 ;
left: 0 ;
width: 100% ;
height: 100% ;
}
To create an adaptive design, media queries are often used (they set rules based on the width of the screen - based on the screen resolution).
Here is a sample media queries - what resolutions to use for adaptive design:
@media only screen and (max-width: 1200px) (
@media only screen and (max-width: 992px) (
/* Small Devices, Tablets */
@media only screen and (max-width: 768px) (
@media only screen and (max-width: 480px) (
/* Custom, iPhone Retina */
@media only screen and (max-width: 320px) (
/**/
}
/*========== Mobile First Method ==========*/
/* Custom, iPhone Retina */
@media only screen and (min-width: 320px) (
/**/
}
/* Extra Small Devices, Phones */
@media only screen and (min-width: 480px) (
/**/
}
/* Small Devices, Tablets */
@media only screen and (min-width: 768px) (
/**/
}
/* Medium Devices, Desktops */
@media only screen and (min-width: 992px) (
/**/
}
/* Large Devices, Wide Screens */
@media only screen and (min-width: 1200px) (
/**/
}
But you can also avoid media queries by setting the width of columns and blocks in percentages.
For media queries, we start from the top: everything we did is acceptable for max-width: 768 will also work at 480.
What are the problems when adapting websites for mobile devices?For example, Yandex can show this - There is horizontal scrolling:
You have something with padding or margin - reset them to zero for parent selectors (blocks) and you will be happy.
And at the end, Yandex Webmaster shows this:

I also did it for 4 hours, the first time is always difficult! But then, you can do it in just a couple of hours! And we send it to the webmaster for re-checking, so that it’s faster - important for SEO.
In general, today many people use ready-made templates - Bootstrap and there is practically no pain -
Adaptive layout The site allows web pages to automatically adjust to the screens of tablets and smartphones. Mobile Internet traffic is growing every year, and in order to effectively process this traffic, you need to offer users responsive websites with a user-friendly interface.
Search engines use a number of criteria to evaluate a site's responsiveness when viewed on mobile devices. Google is trying to simplify the use of the Internet for owners of smartphones and tablets, marking sites adapted for mobile devices with a special mark mobile-friendly in mobile search results. Yandex also has an algorithm that gives preference to sites with a mobile/responsive version for users in mobile search.
You can check the display of the page on mobile devices on the services and.
 Rice. 1. Mobile search results from Yandex and Google with a note about the site’s friendliness to mobile devices. What is adaptive layout?
Rice. 1. Mobile search results from Yandex and Google with a note about the site’s friendliness to mobile devices. What is adaptive layout? Adaptive layout assumes the absence of a horizontal scroll bar and scalable areas when viewed on any device, readable text and large areas for clickable elements. Using media queries, you can control the layout and placement of blocks on the page, rebuilding the template so that it adapts to your needs. different sizes device screens.
Basic techniques for creating a responsive website are given in the article. For responsive design, the width of the main site container is set in %, and it can be equal to 100% of the browser window width or less. The width of the grid columns is also specified in %. In responsive design, the width of the main container and grid columns is fixed using px values.
The adaptive fluid layout technique discussed in this lesson will work perfectly on a two-column template, making the site adaptive and convenient for viewing on mobile devices. The template assumes a different layout of the main content of the pages; in this lesson the layout of the main page will be discussed.
Home page layoutA page consists of three main blocks: a header (header), a wrapper container for the main content and sidebar, and a footer (footer). Let's take 768px and 480px as design turning points.
At the first point, we will hide the top menu and move the sidebar under the container with posts. At the second point, we will change the location of the header elements, cancel the positioning of social network buttons in posts, and cancel the wrapping of the page footer columns.
 Rice. 2. Example of adaptive layout 1. Meta tags and section
Rice. 2. Example of adaptive layout 1. Meta tags and section 1) Add the necessary files to the section - a link to the fonts used, the jQuery library, as well as the prefixfree plugin (so as not to write browser prefixes for properties):
Adaptive website layout
2. Page headerWe will place the following container elements in the page header:
logo ;
button to show/hide the main menu;
Main menu
L O G O
3. Block with a summary of the articleWe will wrap the announcement of articles with the element:
 Design Spring
Design Spring
The Russian language is very rich in words relating to the seasons and the natural phenomena associated with them.
Continue reading ... 4. SidebarIn the side column we will add a list of categories, recent posts and a newsletter subscription form:
Categories
The last notes Subscribe to the newsletter 5. FooterIn the footer of the page we will place copyright information, social network buttons and a link to email:
My blog © 2016 Write a letter $(".nav-toggle").on("click", function())( $("#menu").toggleClass("active"); ));
6. General CSS stylesGeneral styles, reset browser styles to default:
*, *:after, *:before ( box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0; margin: 0; transition: .5s ease-in-out; /* add smooth transitions for all page elements */ ) ul ( list-style: none; ) a ( text-decoration: none; outline: none; ) img ( display: block; width: 100%; ) h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, h6 ( font-family: "Playfair Display"; font-weight: normal; letter-spacing: 1px; ) body ( font-family: "Open Sans", arial, sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 1; color: #373737; background: #f7f7f7; ) /* add flow cleanup for all containers that have child elements wrapped inside them */ header:after, .container:after, footer:after, .widget-posts-list li:after, #subscribe:after ( content: ""; display: table; clear: both; ) /* style class that controls the width of the grid container */ .container ( margin: 0 auto; width: 100%; max-width: 960px; padding: 0 15px ; )
7. Styles for the header and its contents header ( width: 100%; background: white; box-shadow: 3px 3px 1px rgba(0,0,0,.05); padding: 15px 0; margin-bottom: 30px; position : relative; ) /* logo */ .logo ( display: block; float: left; ) .logo span ( color: white; display: inline-block; width: 30px; height: 30px; line-height: 30px; border -radius: 50%; margin: 5px 0; text-align: center; text-shadow: 2px 2px 1px rgba(0,0,0,.4); logo span:nth-child(odd) #EF5A42; ) .logo span:nth-child(even) ( background: #F8B763; ) /* menu */ #menu ( float: right; ) #menu li ( display: inline-block; margin-right: 30px; ) #menu a ( color: #111; text-transform: uppercase; letter-spacing: 1px; font-weight: 600; display: block; line-height: 40px; ) #menu a:hover ( color: #EF5A42; ) #menu li:last-child ( margin-right: 0; ) /* search form */ #searchform ( float: right; margin-left: 46px; display: inline-block; position: relative; ) #searchform input ( width: 170px; float: left; border: none; padding-left: 10px; height: 40px; overflow: hidden; outline: none; color: #9E9C9C; font-style: italic; ) #searchform button ( background: transparent; height: 40px; border: none; position: absolute; right: 10px; color: #EF5A42; cursor: pointer; font-size: 18px; ) #searchform input:focus ( outline: 2px solid #EBEBE3; ) /* menu toggle button appearing at 768px width */ .nav-toggle ( display: none; position: relative; float: right; width: 40px; height: 40px; margin-left: 20px; background: #EF5A42; cursor: pointer; ) .nav-toggle span ( display: block; position: absolute; top: 19px; left: 8px; right: 8px; height: 2px; background: white; ) .nav-toggle span:before , .nav-toggle span:after ( content: ""; position: absolute; display: block; left: 0; width: 100%; height: 2px; background: white; ) .nav-toggle span:before ( top: -10px; ) .nav-toggle span:after ( bottom: -10px; ) /* class that will be added to the top menu when the button is clicked and will show the hidden menu */ #menu.active ( max-height: 123px; ) 8. Styles for the main content block /* left container */ .posts-list ( margin-bottom: 30px; width: 64%; float: left; ) /* block for the article */ .post ( margin-bottom: 35px; ) .post-content p ( line-height: 1.5; padding-bottom: 1em; ) .post-image ( margin-bottom: 30px; ) . category ( margin-bottom: 15px; ) .category a ( color: #F8B763; text-transform: uppercase; ) .post-title ( margin-bottom: 12px; font-size: 26px; ) /* block with the "continue" button reading" and social network buttons */ .post-footer ( border-top: 1px solid #EBEBE3; border-bottom: 1px solid #EBEBE3; position: relative; margin-top: 15px; ) .more-link ( position: relative ; display: inline-block; text-transform: uppercase; line-height: 0 22px; letter-spacing: 0. 1em; white-space: nowrap; ) .more-link:after ( content: ""; display: block; position: absolute; width: 0; height: 0; top: 0; right: 0; border: solid transparent; border-width: 22px 18px; border -left-color: #3C3D41; transform: translateX(100%) ) .post-social ( position: absolute; left: auto; top: 50%; right: 0; text-align: right; transform: translateY(- 50%); padding: 0; font-size: 12px; .post-social a ( display: inline-block; margin-left: 8px; color: #F8B763; width: 25px; height: 25px; line-height: 23px; text-align: center; border-radius: 50%; border: 1px solid); */ .widget ( padding: 20px 15px; background: white; font-size: 13px; margin-bottom: 30px; box-shadow: 3px 3px 1px rgba(0,0,0,.05); ) .widget-title ( font-size: 18px; padding: 10px; margin-bottom: 20px; text-align: center; border: 2px solid #F8B763; box-shadow: 3px 3px 0 0 #F8B763; ) .widget-category-list li ( border-bottom: 1px solid #EBEBE3; padding: 10px 0; color: #c6c6c6; font-style: italic; ) .widget-category-list li:last-child ( border-bottom: none; ) .widget-category-list li a ( color: #626262; margin-right: 6px; font-style: normal; ) .widget- category-list li a:before ( content: "\f105"; display: inline-block; font-family: "FontAwesome"; margin-right: 10px; color: #c6c6c6; ) .widget-posts-list li ( border -top: 1px solid #EBEBE3; padding: 15px 0; ) .widget-posts-list li:nth-child(1) ( border-top: none; ) .post-image-small ( width: 30%; float: left; margin-right: 15px; .widget-post-title ( float: left; ) /* subscription form */ #subscribe ( position: relative; width: 100%; padding: 15px 0; ) #subscribe input ( width : 100%; float: left; font-style: 0 0 10px; #subscribe button ( padding: 0 15px; background: transparent; height: 40px; border: none; position: absolute; right: 0; color: #EF5A42; cursor: pointer; font-size: 18px; ) #subscribe input: focus + button ( background: #EF5A42; color: white; ) 10. Footer stylesWe divide the site footer into three equal columns:
Footer ( padding: 30px 0; background: #3C3D41; color: white; ) .footer-col ( width: 33.3333333333%; float: left; ) .footer-col a ( color: white; ) .footer-col:last- child ( text-align: right; ) .social-bar-wrap ( text-align: center; ) .social-bar-wrap a ( padding: 0 7px; font-size: 18px; )
11. Media queries @media (max-width: 768px) ( /* show the button to toggle the top navigation */ .nav-toggle ( display: block; ) header ( padding: 10px 0; ) /* hide the top menu, cancel wrapping, position it, moving it to the height of the site header */ #menu ( max-height: 0; background: white; float: none; position: absolute; overflow: hidden; top: 63px; right: 0; left: 0; margin : 0; padding: 0; z-index: 3; ) /* make the list elements block so that they are located under each other */ #menu li ( display: block; text-align: center; border-bottom: 1px solid # EBEBE3; margin-right: 0; ) /* cancel the wrapping of the left and right columns, set their width to 100% */ .posts-list, aside ( width: 100%; float: none; ) .widget-post-title ( font -size: 1.5em; ) ) @media (max-width: 480px) ( /* cancel the wrapping for the logo and align it to the center */ .logo ( float: none; margin: 0 auto 15px; display: table; ) .logo span ( margin: 0 2px; ) /* position the menu to the increased height of the header */ #menu ( top: 118px; ) /* position the search form to the left */ #searchform ( float: left; margin-left: 0; ) /* remove the top and bottom borders and align the button to the center */ .post-footer ( border-top: none; border-bottom: none; text-align: center; ) /* cancel the positioning of social media buttons */ .post-social ( position: static; text-align: center; transform: none; margin-top: 20px; ) .widget- post-title ( font-size: 1.2em; ) /* cancel wrapping for page footer columns */ .footer-col ( float: none; margin-bottom: 20px; width: 100%; text-align: center; ) . footer-col:last-child ( text-align: center; margin-bottom: 0; ) ) 12. Script for the mobile menuThe jQuery code that we previously added to the page markup before the closing tag is responsible for showing and hiding the top menu when the button is clicked (the height of the menu is switched from zero to equal to its contents):
$(".nav-toggle").on("click", function())( $("#menu").toggleClass("active"); ));
Adaptive website layout - lessons for beginners. More and more often, readers of the Web Council blog ask questions in their letters about adaptive website layout. OK! If you have any questions, then welcome! With this post, I am opening a new section on the blog, dedicated exclusively to adaptive website design.
For those who are not in the tank and are hearing about this newfangled (since 2012) feature for the first time, a brief explanation:
Adaptive layout is designed to automatically adjust the site to different screen sizes of display devices: desktop PCs, TVs, tablets, smartphones and other mobile phones.
One very important clarification should be given here regarding the various similar definitions in modern web design, namely: adaptive (adaptive) and responsive (responsive) web design. Many people mistakenly believe that these are the same thing. But that's not true.
Adaptive vs responsiveFirstly, it is necessary to distinguish adaptive web design And adaptive layout. These are completely different concepts. Adaptive web design is a global approach to website design, while adaptive layout is just a special case of a layout method for responsive web design.
Adaptive and responsive web design are like night and day. Moreover, we can safely say that responsive web design is a small part (albeit quite self-sufficient) of responsive web design.
The main difference in terms of layout is the way the style file is written. Responsive assumes that everything is completely written in the style file possible options sizes of the viewing devices used, while adaptive loads only those styles that are necessary for each specific type of device.
Moreover, a responsive one loads the same amount of site details for both a desktop PC and a mobile phone, optimizing the sizes of blocks and their contents, while an adaptive one can load the entire site for such a PC, but only a part for a mobile phone, deleting something, if not very important to facilitate the design of the site and, accordingly, increase loading speed.
There is no point in harping on this topic anymore. Suffice it to say that today, responsive web design is in great demand, but with adaptive layout :) I hope that after this short excursion Now you will not be confused in concepts. For those who want to familiarize themselves with this topic in more detail, I can recommend reading and.
OK! We've sorted out the definitions. Let's continue the story about adaptive website layout, implying that we're talking about about responsive web design.
Advantages of adaptive layoutAdaptive website layout has two main weapons in its arsenal:
1. All layout elements are “rubber” (flexible)- their sizes depend on the screen size of the display device.
2. Media Queries- a separate part of the style file, which specifies different styles depending on the size of the screens of display devices and their location in space (portrait or landscape).
As for the “rubberiness”, this bun is set in the good old way:
In addition, to prevent the site from being smeared on too large monitors, the following rule is written in the style file:
#content (
max-width: 1200px;
}
This is if you don't want the site width to exceed 1200px (up to you). There is a certain sensation in this. The fact is that a comfortable readable text width is no more than 10–12 words per line. If the article stretches (for example, when viewing the site on a TV) from edge to edge, then reading such text will be very difficult.
In adaptive layout, the rule is not only to use fluidity for large blocks, but also for media content: pictures, video inserts, etc. This can also be easily specified in styles:
img, embed, video (
max-width: 100%;
}
When the browser window is reduced, all pictures, videos and other elements will be proportionally reduced without extending beyond the edges of the parent block.
But we’ll talk about media queries in detail next time. Stay in touch!
Adaptive website layout | Introduction
From the author: in the future, a constant increase in mobile traffic is expected in the Internet world. This means that now you need to be able to create layouts so that your project looks good on all devices. The solution has long been found - adaptive website layout! We'll talk about her.
2 ways to please mobile usersThe simplest way determining how the site is laid out is to reduce the size of the window. If appeared horizontal stripe scrolling, which means this is a fixed layout. All sizes were most likely specified in pixels. Will this site be convenient for users on mobile devices? No.
Essentially, there are two solutions to this problem. The first is to create different versions of the layout (for PCs, for tablets and for mobile phones). This is exactly what was done, for example, in social network In contact with. The second option is to make adaptive layout. Such a site will respond to changes in the window width. This option is being used more and more often today.
Rice. 1. As you can see, even on mobile phone webformyself displays well.
Adaptability is the beginning of the journeyAdaptive layout is no different from regular layout, except that media queries are added to the style sheet, where styles are specified for different screen widths. Sometimes they are placed in a separate css file, and sometimes they are written at the end of the main style sheet. Example media query:
@media only screen and (max-width: 980px)()
@media only screen and (max - width: 980px) ( ) |
Let's take a closer look at this entry.
@media – the actual designation of the media query
Screen – we indicate that this refers to the screen (here you can also specify a TV or projector). Only – means that the rules will be applied only to screen.
And (and) – adding a condition for which the media query will work. The condition is added in parentheses.
Max-width: 980px – the condition itself. In simple terms, this means that the media query will work when the screen width is a maximum of 980 pixels (that is, from 0 to 980px). If the width is greater than 980, the rules will not work. Most often, the conditions here are max-width, min-width, max-device-width, min-device-width. The last two mean that the rules will only work on the mobile devices themselves (that is, when changing the window width on a computer, a horizontal scroll will appear). You can also specify max-height, but this is used very rarely.
() – all the CSS rules are written in these curly braces. There can be as many of them as you like. Let me give you a couple of examples to make it clear to you:
@media only screen and (max-width: 980px)( .selector(background: black) ) @media only screen and (min-width: 600px)( img(float: left) )
@media only screen and (max - width: 980px) ( Selector (background: black) @media only screen and (min - width: 600px) ( img (float: left) |
Let's translate it into human language: if the window width is less than 980 pixels, then the rule (background: black) will be applied to the element with the selector class. In even simpler terms, the background of this element will become black.
Second example: if the window width is more than 600 pixels, then all images will be pressed to the left edge.
Have you already realized the genius of this layout method? Essentially, with the help of media rules, you can adjust existing or add new CSS rules. This way you can implement a fully responsive template.

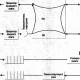
Rice. 2. An example of a media query that specifies rules for widescreen monitors.
Learn more about adaptabilityThis is understandable, but how to make adaptive website layout yourself? To do this, it is clearly not enough for you to write down those two examples. I hope you get the gist of them, but they are of little use. We need real benefits. And you can get it from. But this is if we take adaptability seriously. The fact is that since the course is paid, after studying it you yourself will be able to teach others adaptive layout.
If you need something simpler just to get the hang of it, this one will suit you much better. It consists of five video lessons that will walk you through the basics. The course is very easy, the information is selected specifically for beginners. At the same time, you will be able to look at several practical examples, so after studying it you can adapt a simple layout yourself.
Is it difficult to master adaptive layout?When I first started studying web technologies, I didn’t even really know what adaptive website layout was. It was not possible to do this on my own. Fear is our main enemy. It turned out that everything was quite simple. And now, when I sometimes look at the code adaptive templates, I understand how adaptability is sometimes easy to implement.
How to test adaptabilityThe easiest way to do this is in the browser. For example, in my Google Chrome When you press F12 the debugger appears. Now try resizing the window. In the upper right corner you will see the value of its width. This is very convenient for quickly checking your layout. I can also recommend responsivetest.net. The service is quite convenient and perfectly tests adaptability.

Rice. 3. When you hold down F12, the debugger appears. Now in the upper right corner you can see the current width of the window when changing.
Why adaptive layout?At the beginning of the article, I said that there is another way to please mobile users - to develop separate versions for various devices. What do you think is the easiest way? Adaptability is much easier to implement. This is just a couple hundred extra lines of code, rather than a separate version of the site, which is often very different in design. As practice shows, mobile versions Only large companies that can afford to spend money do this for their websites. more money for the development of the project.
For everyone else, adaptive layout is something to strive for now. And since mobile traffic will only grow, start implementing it now. And at the same time, subscribe to our blog to improve your knowledge in website building.
For those who have not yet heard of such a term as adaptive layout, I can say that such layout can be called obedient in human language. This type of layout adapts to all possible screens of the devices from which your visitor came, and lately there are a lot of them, to put it mildly (netbooks, tablets, iPhones, Android-based devices...). All of these devices have a feature, they work with different screens, but some of them are even rebuilt individual elements, for example, the iPhone is very inappropriate; it makes its own buttons and form fields on your website for your design.
Adaptive layout - where to startLet's talk in order about where to start making adaptive layout and what difficulties there may be.
What to use for layout:
I think I won’t be wrong if I say that you need to start by studying simple definition browser using CSS3. That is, so that you can build different styles for different device screens, and your design changed when the browser window narrowed so that site visitors would be comfortable working with it.
These are the styles that will be enough for you to get started:
Adaptive css for website layout
/* For large screens */ @media (min-width: 1200px) ( ... ) /* For some netbooks and tablets */ @media (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 979px) ( ... ) /* For tablets and some phones */ @media (max-width: 767px) ( ... ) /* For phones and some devices with very small screens */ @media (max-width: 480px ) (...)
/* For large screens */ @media (min - width: 1200px) (...) /* For some netbooks and tablets */ @media (min - width: 768px) and (max - width: 979px) (...) /* For tablets and some phones */ @media (max - width: 767px) (...) /* For phones and some devices with very small screens */ @media (max - width: 480px) (...) |
Using the above code, you can set the settings for individual blocks and style them for different device screens, but in addition, it is necessary that the devices understand that your site is made for them. The viewport code can help us with this.
viewport - for mobile devices
< meta name = "viewport" content = "width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" > < link href = "assets/css/bootstrap-responsive.css" rel = "stylesheet" > |
The above code will not allow the user to enlarge or reduce your site as he wants; the styles we talked about above should do this for him.
Bonus in favor of responsive sitesSearch engines are already much better at recognizing responsive sites and changing the results for them. That is, your site, made according to the rules of adaptive layout, will most likely be higher for those who are looking for information on mobile devices than simple and boring sites that need to be reduced and enlarged on the screen in order to read anything on them. This conclusion came to me from the experience of developing a website for a law firm and analyzing its statistics. Google and Yandex love user-friendly sites, but given that such sites cost 3–4 times more, not everyone can afford to order adaptive design and development for this design. The cost is due to the fact that you need to draw a design for 3-4 devices and also layout for different devices, and CSS frameworks like Bootstrap cannot always solve all the tasks that the client did not come up with).
Let's talk a little about BootstrapThe first thing I wanted to say about Bootstrap is, don’t look for documentation anywhere other than the official website, their documentation there is so well described that it’s unlikely that anyone can better describe all the features of this mega-framework step by step. The speed of layout increases significantly, but only if the client needs a simple website without any inventions. But when a website is made according to all the client’s requirements, sometimes it is better to leave this framework and start doing everything simply by hand. The framework is perfect for those who want to learn how to make interfaces, for example, for admin panels, where the uniqueness of the design does not play a big role, but everything needs to be made convenient. The backend of the site made with bootstrap turns out to be very convenient and concise, I highly recommend it.
Texts in adaptive layoutIn order for the site to look good on all screens, it is not enough just to rebuild the blocks, change their size and purpose when css help frameworks and JavaScript, you also need to remember how text behaves on different screens. If on small screen phone at 480 pixels, the text looks good at 12 pixels, then on bigger screen this text needs to be enlarged, since on large monitors no one looks at the text directly, but reads it from afar. After some searching on the Internet, I found an excellent plugin written in jqery. The plugin is called FitText and is located. All you need to do is connect the plugin and call it on the desired page elements.
Example of using fittext
$("#fittext1").fitText();
$("#fittext1") . fitText(); $("#fittext2") . fitText(1.5); $("#fittext3") . fitText (1.1, (minFontSize: 50, maxFontSize: "75px")));
|
The plugin has one feature: it only works with block elements(block, block-inline).
Problems with adaptive layout:So far I haven’t noticed any more difficulties with this, but if you know, write, I will check and add to it. Sometimes in some cases you need to determine the device type before loading the page in the browser, in such cases I advise you to use a class written in PHP. The script will help determine the screen size of a site visitor and the device from which he visited before loading the site, on the server side. .
If you need your blocks to change smoothly on your site, you can use CSS3 animation in your styles for all blocks.
Smooth transformation of CSS3 blocks
*( -webkit-transition: all 0.3s ease; -moz-transition: all 0.3s ease; -o-transition: all 0.3s ease; -ms-transition: all 0.3s ease; transition: all 0.3s ease; )
Webkit - transition : all 0.3s ease ; Moz - transition : all 0.3s ease ; O - transition : all 0.3s ease ; Ms - transition : all 0.3s ease ; transition : all 0.3s ease ; |
If your design does not allow for a smooth transformation of all elements on the page, then you can simply replace (*) with (any arc element) or disable animation for individual blocks as in the example below.
transition - cancel transformation
Class-block, .class-block * ( /*CSS transitions*/ -o-transition-property: none !important; -moz-transition-property: none !important; -ms-transition-property: none !important; - webkit-transition-property: none !important; transition-property: none !important; /*CSS transforms*/ -o-transform: none !important; ; -webkit-transform: none !important; transform: none !important; /*CSS animations*/ -webkit-animation: none !important; ms-animation: none !important; animation: none !important )
Class - block , . class - block * ( /*CSS transitions*/ O - transition - property : none ! important ; Moz - transition - property : none ! important ; |

 Summer
Summer Autumn
Autumn