0 001 bytes how many bits. Measuring information. What is larger: kilobyte or megabyte?
In order to thoroughly understand what Bits are, what Bytes are and why all this is needed, let’s first dwell a little on the concept of “Information”, since this is what the work is based on computer technology and data networks, including our beloved Internet.
For a person, Information is some knowledge or information that people exchange in the process of communication. At first, knowledge was exchanged orally, passed on to each other, then writing appeared and information began to be transmitted using manuscripts, and then books. For computing systems, Information is data that is collected, processed, stored and transmitted further between parts of the system, or between different computer systems. But if earlier information was placed in books and its volume could be at least somehow visually assessed, for example in a library, then in conditions digital technologies it has become virtual and cannot be measured using the usual and familiar metric system to which we are accustomed. Therefore, units of information measurement were introduced - Bits and Bytes.
Bit of information
In a computer, information is stored on special media. Here are the most basic and familiar to most of us:
Hard drive (HDD, SSD) - optical disk(CD, DVD) - removable USB drives (flash drives, USB-HDD) - memory cards (SD, microSD, etc.)
Your Personal Computer or the laptop receives information, mainly in the form of files with varying amounts of data. Each of these files is received, processed, stored and transmitted by any data carrier at the hardware level in the form of a sequence of signals. There is a signal - one, no signal - zero. Thus, all information stored on the hard drive - documents, music, films, games - is presented in the form of zeros: 0 and ones: 1. This number system is called binary (only two numbers are used).
Here is one unit of information (it makes no difference whether it is 0 or 1) and is called bit. The word itself bit came to us as an abbreviation for bi nary digi t — binary number. What is noteworthy is that English language there is a word bit - a little, piece. Thus, a bit is the smallest unit of information.
How many bits are in a byte
As you already understood above, a bit in itself is the smallest unit in the information measurement system. That is why it is completely inconvenient to use it. As a result, in 1956, Vladimir Buchholz introduced another unit of measurement - Byte, like a bundle of 8 bits. Here clear example byte in binary system:
00000001 10000000 11111111
Thus, these 8 bits are a Byte. It is a combination of 8 digits, each of which can be either a one or a zero. There are 256 combinations in total. Something like that.
Kilobyte, Megabyte, Gigabyte
Over time, the volume of information has grown, and in recent years, exponentially. Therefore, it was decided to use the prefixes of the SI metric system: Kilo, Mega, Giga, Tera, etc.
The prefix “kilo” means 1000, the prefix “mega” means million, “giga” means billion, etc. At the same time, it is impossible to draw analogies between an ordinary kilobit and a kilobyte. The fact is that a kilobyte is not a thousand bytes, but 2 to the 10th power, that is, 1024 bytes.
Accordingly, a megabyte is 1024 kilobytes or 1048576 bytes.
A gigabyte is equal to 1024 megabytes or 1048576 kilobytes or 1073741824 bytes.
For simplicity, you can use the following table:
As an example, I would like to give these numbers:
A standard A4 sheet with printed text takes up about 100 kilobytes on average.
An ordinary photograph on a simple digital camera - 5-8 megabytes
Photos taken with a professional camera - 12-18 megabytes
A music track in mp3 format of average quality for 5 minutes - about 10 megabytes.
An ordinary 90-minute film, compressed in normal quality - 1.5-2 gigabytes
The same film in HD quality - from 20 to 40 gigabytes.
P.S.:
Now I will answer the questions that beginners most often ask me.
1. How many Kilobits are in a Megabit? The answer is 1000 kilobits (SI system)
2. How many Kilobytes are in a Megabyte? The answer is 1024 Kilobytes
3. How many Kilobits are in a Megabyte? The answer is 8192 kilobits
4. How many Kilobytes are in a Gigabyte? The answer is 1,048,576 Kilobytes.
Tweet
Plus
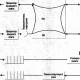
First, let's try to figure out what bits and bytes are. A bit is the smallest unit of measurement of the amount of information. Along with a bit, a byte is actively used.
A byte is equal to 8 bits. Let's try to depict this clearly in the following diagram.
I think this is all clear and there is no point in going into more detail.
In simple terms, connection speed is the amount of information received or sent by your computer per unit of time. In this case, it is customary to consider the second as the unit of time, and the kilo or megabit as the amount of information.
So if your speed is 128 Kbps it means your connection has throughput 128 kilobits per second or 16 kilobytes per second.
Whether this is a lot or a little is up to you to judge. In order to get a more tangible sense of your speed, I recommend using our tests. Determine the time required to download a file of a specified size at your connection speed. You can also see how large a file you can download within a certain period of time at your connection speed.
When using our tests, you must remember and take into account that our server, on which all these tests are actually located, is located quite far from your computer and, accordingly, the results can be affected by the load on our server (on our website during peak hours, they simultaneously measure connection speeds of more than 1000 people), and the congestion of Internet lines.
Units for measuring the amount of information Basic: 1 bit - 0 or 1 1 byte = 8 bits Derivatives: 1 KB (Kilobyte) = 1024 bytes 1 MB (Megabyte) = 1024 KB 1 GB (Gigabyte) = 1024 MB 1 TB (Terabyte) = 1024 GB Larger: 1 Petabyte, 1 Exabyte, 1 Zetabyte, 1 Yotabyte

Bit Bit Byte Byte KilobyteKilobyte Megabyte Megabyte Gigabyte Gigabyte ... into smaller units - MULTIPLY by... *8 *1024 *1024 *1024 /8 /1024 /1024 /1024 ...into larger units - DIVIDE by... Example: 725 bytes = 725 * 8 = 5800 bits 725 bytes = 725 / 1024 = 0.7 Kilobytes Converting information units

1) How many bits are in 1 Kilobyte? 2) How many bytes and bits are there in 5 Kilobytes? 3) Convert 7200 bits to bytes and Kilobytes * 8 = 8192 bits 5 * 1024 = 5120 bytes 5120 * 8 = bits 7200 / 8 = 900 bytes 900 / 1024 = 0.88 KB Solve the problems:

5) Convert 1536 MB to Kilobytes and Gigabytes 0.5 * 1024 = 512 Kilobytes 512 * 1024 = byte * 8 = bit 4) Convert 0.5 Megabytes to Kilobytes, bytes and bits 1536 * 1024 = Kilobyte 1536 / 1024 = 1, 5 Gigabytes

6) How many times is 1 Kilobit 1 Kilobit? 1024 times (compare the prefixes Kilo- and Mega-) 1 Kilobit? 1024 times (compare the prefixes Kilo- and Mega-)"> 1 Kilobit? 1024 times (compare the prefixes Kilo- and Mega-)"> 1 Kilobit? 1024 times (compare the prefixes Kilo- and Mega-)" title="6) How many times is 1 Kilobit 1 Kilobit? 1024 times (compare the prefixes Kilo- and Mega-)"> title="6) How many times is 1 Kilobit 1 Kilobit? 1024 times (compare the prefixes Kilo- and Mega-)"> !}
3 bytes...24 bits 200 bytes...0.25 KB 150 bytes...1100 bits 100 MB...0.1 GB bits...1.5 KB 3.5 KB...3600 bytes = title="3 bytes...24 bits 200 bytes…0.25 KB 150 bytes…1100 bits 100 MB…0.1 GB 12288 bits…1.5 KB 3.5 KB…3600 bytes =
8) Petya Knopkin bought a new film in Blu-Ray format with a capacity of 25 GB, and on his friend Kolya Myshkin’s computer there is still a byte free on the hard drive. Will Kolya be able to record a film on his hard drive? Solution: 1) Translate big number in KB MB GB / 1024 / 1024 / 1024 = 30 GB The film will fit, because 25 
Any person who has interacted with computers at least a little is familiar with such terms as “Gigabyte”, “Megabyte” and others.
They indicate the volume of a physical storage medium, such as a flash drive, hard drive or the volume of any file stored on the computer.
Simply put, this value indicates how much space on a computer any file occupies, or how much information in total the medium can hold.
If you are reading this article with the goal of converting one unit of measurement to another, then I recommend immediately using the free online calculator at the bottom of the page.
Enter any value in the field, select a value from the list and the calculator will perform the conversion.
What is a byte, kilobyte, megabyte, gigabyte
Several decades ago, computer memory was small, amounting to no more than a dozen bits or a couple of bytes. You could store several formulas, a couple of examples or mathematical expressions there.
Now the volumes hard drives are several terabytes each, and the file sizes are calculated in gigabytes. Therefore, with the progress of computer progress, a problem arose in recording how much memory a document occupies.
It was then that other quantities were invented that completely came out of the term “bit”.
In other words, the terms "byte", "kilobyte", "megabyte" And "gigabyte" are universal units of information volume that indicate how much space files take up on your hard drive.
How does it work?
All hard drives, SD cards, flash drives can be combined under one common name - physical media.
In simple terms, all these physical media consist of small cells for storing information.
They contain data that is transferred to it using binary code. These cells are called bits, and they are the smallest amount of computer information.

When you transfer information to a medium, it is, as it were, recorded in these memory cells and begins to take up space.
Actually, the file size indicates how many bytes will be used when storing a particular file. This is the principle of volume designation.
In addition, data that is used in the system is temporarily recorded in a special memory area - operational memory.
They remain there as long as they are needed and are then unloaded. Data is written there to exactly the same cells, so RAM has its own volume designation, albeit much smaller than hard drives.
What is larger - megabit or megabyte
Often, the description of USB ports on the motherboard, as well as the characteristics of flash cards and other portable media, indicate the information transfer speed.
It is designated as Gb/sec or Mb/sec, but do not confuse them - it is not gigabyte/second or megabyte/second.
In this case, this is how other units of measurement are designated – megabits and gigabits.
With their help, the speed of information transfer is measured.
These quantities are much smaller than megabytes and gigabytes, and they are calculated, unlike the above-mentioned volumes, in the decimal number system.
One megabit is equal to approximately a million bits. One gigabit is equal to a billion bits of information.
You can almost always see these designations in the speeds of Internet providers.

Therefore, if the speed of your network is 100 Mbit/s, then in one second of connection, 1,000,000 * 100 bits of information will arrive on your computer.
Internet connection technologies make it possible to offer users not megabit, but gigabit connection options.
USB 3.0 port standards allow you to transfer information at a speed of 5 Gbit/sec, and this is far from the limit - after all, motherboards connectors of higher and higher speed versions appear.
It is worth noting that the question of what is larger: a megabit or a megabyte is incorrect and cannot be answered.
This different sizes, different ways measurements. Although they are compared with each other, however, no one does this, since it has no meaning or practical use.
How many megabytes are in a gigabyte
More and more comes out of less. Thus, a group of eight bit cells creates one large byte cell, that is, 8 bits = 1 byte.
- 1024 bytes = 1 kilobyte,
- 1024 kilobytes = 1 gigabyte,
- 1024 gigabytes = 1 terabyte.
Large volumes are not used in home PCs, so there is little point in talking about them.
The average user will immediately have a logical question - why are the calculations and gradations so strange?
Wouldn't it be simpler to make 10 bits equal to 1 byte, and 1 gigabyte equal to 1000 megabytes?
Yes, indeed, it would be much easier. However, it is simpler in the number system we are familiar with.
Here's the thing. In the real world we use a range of numbers from 0 to 9. This is called decimal system Reckoning But computers think differently: they only know two numbers - 0 and 1, that is their calculation system is binary.
These numbers, conventionally, mean “Yes” or “No”. In this case, they show whether the information storage cell is full or not.
Without going into mathematics, it is only worth saying that when converting numbers from a binary system understandable to a computer into our decimal system, two is raised to a certain power.
And to the power of two there are no numbers that are multiples of 10. That is why the calculations are so strange: 1 byte in this case is equal to 2 to the 3rd power of bits and so on.
Thus, the gradation is carried out from two, and the number is greater, the more large quantity times it is multiplied by itself.
Why is a 1GB HDD not equal to 1000MB
Based on the explanation above, one gigabyte is greater than a thousand megabytes by exactly 24 units. Therefore, in the characteristics on hard drives They write exactly how much their volume is. These values cannot be rounded either.
Accordingly, 8 gigabytes of RAM is not 8000 megabytes, but 8192.
It is for this same reason that sometimes when purchasing a storage medium, its volume is slightly less than what is written in the specifications.
There simply cannot be an exact value, so often instead of the promised ten gigabytes, nine are discovered.
Where are these quantities used?
As mentioned above, these terms are used in the computer IT field.
For example, when indicating the capacity of an HDD. Modern hard drives already have a capacity of more than one terabyte, and continue to expand.
With flash cards and other portable media, everything is more modest - their maximum volume can reach 128 gigabytes.
The same terms denote the volume of files.
The spread in this regard is much greater; there are cases when a voluminous and large layer of information weighs several gigabytes, or text file, occupying only a couple of kilobytes.

Things are even more interesting with RAM computer.
Its capacity is also measured in memory cells, and many professional machines are now equipped with several sticks of RAM, overall size which can reach 128 gigabytes.
This is due to the fact that more and more resources are needed to process information - and in order for the program to work stably, there must be a lot of space in temporary memory.
Is there more?
Are there quantities larger than a terabyte? Yes, of course they exist.
- 1024 terabytes is 1 petabyte.
- 1024 petabytes – 1 exabyte.
The fact is that modern technologies have not yet reached the point of creating media, much less files, with a volume and size at least close to these values - therefore, they are used extremely rarely in everyday life.
However, they are widely used for computer calculations in science and high technology.
Considering how quickly technological progress is happening now, it is possible that in a couple of years hard drives with a capacity of 1024 terabytes will appear on the shelves
Conversion table: bit, byte, KB, MB, GB, TB
There is a table of all the quantities that are used in modern hard drives, other storage media, and files.
It was created specifically for the convenience of accurately determining the amount of information and is given below. It includes only those units of measurement that can be seen and applied in real life.
After a terabyte, although measurement is carried out, it is at the level of science and high technology, and not of everyday life.
It is enough to simply determine how many bits per second are transmitted to your computer, divide the resulting value by 8, and then by 1024.
For example, at a speed of 100 Mb/sec, approximately 12 megabytes of information will be transferred to you in one second.
The disadvantage of the table is that it can only be used to determine even values, which can be found infrequently.
In order to accurately determine the weight of a file or the capacity of your hard drive, you can use the online converter, which is presented below.
Online unit converter
Of course, the information presented in the table of values is not enough for comfortable calculations.
There are very few files whose weight will be exactly equal to one gigabyte or a hundred megabytes, and therefore even with this background information, it will be difficult to calculate how much media is needed in order to completely transfer a large document.
It is for this purpose that an online unit converter is installed on this site.
It works very simply - you indicate the volume and the value in which it is expressed. Next, you need to select the value to which you want to convert the number - and the converter will give you the exact value.
Nowadays, high technologies are increasingly seeping into everyday life. But just a few decades ago, computers were considered an expensive product that could only belong to wealthy people.
People who have used a phone, tablet or computer are sure to come across terms such as “byte”, “megabyte” or “gigabyte”. And of course, they begin to ask questions about what exactly they mean and what they are used for. This is what our article will be devoted to.
What is information and where is it located on the device?
Information is one of the most expensive and valuable goods, and in some cases it can act as the main weapon against another person. It is especially valued among international companies and corporations.
This term directly affected the sphere of high technology, where information is measured in a special way. Anyone who uses any device should know and understand the units of measurement used in such a case.
MB, GB or KB is the amount of information used by a computer and stored on its hard drive. It records both new and deleted old data.
Where is data stored on a computer?
Any personal computer or laptop has a hard drive in which all its existing information is stored. Before defining such concepts as “kilobyte” or “megabyte”, it is necessary to understand the structure of the place where the data is stored.
A hard drive consists of an electric motor, disks, heads, and a set of circuits.

Previously disks (pancakes) in this device there were at least 2 pieces, and their total number could reach 4 or more. Now they have 2 or even 1 such “damn”. This happened due to developments computer technology, which allow you to increase the density of recording information on the medium.
The number of disks has decreased several times, and the amount of information that they can record has increased many times over. The newest versions of hard drives have only one pancake and can contain up to 3 terabytes of information.
Basic units of information

The smallest unit of information is called a bit. It can only take 2 values - 0 or 1.
The next term is "byte". A byte forms a whole block (octet) of information, which consists of 8 bits.
What does the term “kilobyte (KB)” mean? The amount of information stored by a device is always different, and every year it only grows. We can take as an example: Previously, its volume did not exceed 2 gigabytes, but in our time even 4 will not be enough. It is because of this that the values derived from the byte appeared. That is, KB is a derivative of “byte”. Various prefixes are used, including “kilo-”, “mega-”, “giga-” and so on. The size of a KB is 1021 bytes, which is equal to 2 10 bytes.
Derived units
Derived units of information have been added to shorten the notation. Such derivative words are used not only in the field of high technology, but also, for example, in physics, where the meter is used to measure length, and its derivatives are kilometer, nanometer and others. TB, GB, MB and KB are derivatives formed by adding various prefixes:
- tera-;
- giga-;
- mega-;
- kilo-.
These prefixes became widespread back in 1789, when they were used in sciences such as physics. The very first of them were “kilo-” and “mega-”. They are necessary so that the recording of the amount of information is not so voluminous, that is, to make it easier to read. For example, converting 819,200 KB to MB, we get only 100 MB, which is extremely convenient for visual perception.
Translation of derivatives
GB, MB or KB - this is the same information that surrounds us everywhere. All the time, the volume of information in devices increases, and sometimes you have to face the need to transfer it to another level. For greater convenience, you need to familiarize yourself with the first three positions from the table below:

It was said above that 1 byte contains 8 bits, and you need to convert bits to kilobytes a little differently. For example, there are 128 bits that need to be converted into bytes. Since 1 B = 8 bits, the number 128 is divided by 8. The result is the number 16.
A computer, laptop or any other device perceives information only in its own language. In computer science, there is such an area as programming, and programmers write all their work in the language of the source device, to a greater extent this is binary system, although in this area another one is used - the hexadecimal number system.
Converting from bits to kilobytes is not so complicated, but there are other nuances. Some computer users may be confused about how many KB are in MB or how many GB are in 1 TB. The latter term has appeared recently due to the significant increase in hard drive capacity. In order not to get confused, you need to consider the table that has already been mentioned above. It should especially be shown to those new to using a computer, which will help clarify some difficult points for them.