Peltier efficiency as an electricity generator. What is a Peltier element, its structure, operating principle and practical application. Operating principle of modules
> Generators > Thermoelectric generator
A huge number of electronic devices absorb electrical energy, which must be constantly renewed. While on the road, you have to carry chemical current sources with you or generate electricity from mechanical energy using complex and bulky devices.
Type of thermoelectric generator
Even earlier, Seebeck discovered the occurrence of thermo-EMF in a circuit of dissimilar conductors when maintaining different temperatures at the point of contact.
Based on thermoelectric effects, a so-called Peltier element or module was created, which consists of 2 ceramic plates with a bimetal located between them.
When applying through them electric current, one side of the plate is heated and the other is cooled, making it possible to create refrigerators from them. The figure below shows the modules different sizes, used in technology.
Peltier modules of different sizes
The process is reversible: if you maintain a temperature difference across the elements on both sides, they will generate an electric current, which allows the device to be used as a thermoelectric generator to generate a small amount of electricity.
The Peltier effect is the release of heat at the point of contact of dissimilar conductors when electric current flows through them.
Operating principle of modules
At the contact of dissimilar conductors, heat is released or absorbed depending on the direction of the electric current. The flow of electrons has potential and kinetic energy. The current density in the contacting conductors is the same, but the energy flux densities are different.
If the energy flowing into the contact is greater than the energy flowing out of it, this means that electrons are slowed down at the point of transition from one region to another and heat up the crystal lattice (the electric field slows down their movement). When the direction of the current changes, the reverse process of electron acceleration occurs, when energy is taken from the crystal lattice and its cooling occurs (the directions of the electric field and the movement of electrons coincide).
The energy difference of charges at the boundary of semiconductors is the highest and the effect manifests itself most strongly there.
Peltier module
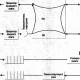
The most common is the thermoelectric module (TEM), which is p- and n-type semiconductors connected to each other through copper conductors.
Diagram of the operating principle of the module
In one element there are 4 transitions between metal and semiconductors. In a closed circuit, the flow of electrons moves from the negative pole of the battery to the positive, sequentially passing through each transition.
Near the first copper-p-type semiconductor transition, heat is released in the semiconductor zone as electrons move to a state with lower energy.
Near the next boundary with the metal in the semiconductor, heat is absorbed due to the “sucking out” of electrons from the p-conductivity zone under the influence of an electric field.
In the third transition, electrons enter the n-type semiconductor, where they have higher energy than in the metal. In this case, energy is absorbed and the semiconductor is cooled near the transition boundary.
The last transition is accompanied by a reverse process of heat release in the n-semiconductor due to the transition of electrons to a zone with lower energy.
Since the heating and cooling transitions are in different planes, the Peltier element will be cooled from above and heated from below.
In practice, each element contains a large number of heating and cooling transitions, which leads to the formation of a noticeable temperature difference, which makes it possible to create a thermoelectric generator.
What does the module structure look like?
The Peltier element contains a large number of p- and n-type semiconductor parallelepipeds, connected in series with metal jumpers - thermal contacts, the other side in contact with the ceramic plate.
Bismuth telluride and silicon germanide are used as semiconductors.
Advantages and disadvantages of TEM
The advantages of a thermoelectric module (TEM) include:
- small sizes;
- the ability to operate both coolers and heaters;
- reversibility of the process when changing polarity, allowing you to maintain an exact temperature value;
- absence of moving elements that usually wear out.
Disadvantages of modules:
- low efficiency (2-3%);
- the need to create a source that provides a temperature difference;
- significant energy consumption;
- high price.
Despite the disadvantages, TEMs are used where large energy costs are not important:
- cooling of chips, parts of digital cameras, diode lasers, quartz oscillators, infrared detectors;
- the use of TEM cascades to achieve low temperatures;
- creation of compact refrigerators, for example, for cars;
- thermoelectric generator for charging mobile devices.
If the productivity of TEG is low, it is advisable to use it in field conditions, where it is necessary to obtain electricity for charging. cell phone or LED light bulb. The simplicity of the design allows you to make an electric generator with your own hands.
Alternative sources are also solar panels or a wind generator. The former require special conditions - the presence of sunlight, which may not always be available. Another source is large and requires wind. Another disadvantage is the presence of moving parts that reduce reliability and are heavy.
Industrial thermogenerators
BioLite has developed new model for hiking, allowing you to cook food in a compact, portable wood-burning stove and at the same time charge your mobile device from the built-in TEG.
Compact portable wood stove
The device will come in handy everywhere: fishing, hiking, at the dacha. Anything that burns can be used as fuel.
When fuel is burned in the furnace, heat is transferred through the wall to the module, which generates electricity.
At a voltage of 5V, the output power is 2-4 W, which is enough to charge many types of mobile devices and operate LED lighting.
The red arrow shows the direction of movement of heat, the blue arrow shows cold air into the furnace, the yellow arrow shows the supply of electricity to rotate the air intake fan and to the generator output via USB.
Scheme of operation of BioLite TEG on wood
The Indigirka generator furnace, developed by the St. Petersburg company Kryotherm, has the following characteristics:
- thermal power – 6 kW;
- weight – 56 kg;
- dimensions – 500x530x650 mm;
- email power at voltage 5V – 60 W.
The stove is a conventional heating and cooking stove, with thermoelectric generators attached on both sides.
What does the thermoelectric generator furnace "Indigirka" look like?
The device is quite convenient, but the price is impressive - 50 thousand rubles. Although the stove is intended for camping conditions, it will clearly not be affordable for ordinary hunters and fishermen. As a heating system, it is no better than conventional and cheaper models.
If you attach a TEG to a simple stove, the homemade device will work perfectly.
DIY TEG
To assemble a thermoelectric generator with your own hands, you need the following elements:
- Module. Not all modules can be used to generate electric current, but only those that can withstand heating up to 300-4000C. Having a heating reserve is necessary, since even with slight overheating the element fails. The most common models are the TEC1-12712 type in the form of square plates with a side size of 40, 50 or 60 mm.
If you take the maximum size, it is enough to use one element in a DIY design. The first 3 digits of the marking - 127 - mean how many elements are contained in 1 plate. The last numbers show the maximum permissible current, which is 12 A.
- Boost converter. It is necessary to obtain a constant voltage of 5V. The generator may produce less voltage, which needs to be increased. The devices are produced foreign (types 5V NCP1402 and MAX 756) and domestic (3.3V/5V EK-1674). To charge your mobile phone, you should choose a device with a USB connector.
- Heater. The simplest options are a fire, a candle, a homemade lamp or a miniature stove.
- Cooler. The easiest way is to use water or, in winter, snow.
- Connecting elements. Equipment is needed to create the maximum possible temperature difference between the two sides of the plate. Here the choice is up to the craftsmen; they most often use 2 mugs or pans of different sizes, the handles of which are sawed off and where one is inserted inside the other. A module is placed between them and secured with thermal paste. 2 wires are soldered to it and connected to a voltage converter.
To increase the efficiency of the generator, the bottoms of the metal surfaces of mugs or pans in contact with the generator plate should be polished. In addition, heat-resistant sealant is applied to the spaces between the bottoms of the smaller and larger mugs. Then the heat from heating will be localized at the location of the module.
The wires between the module and the converter are protected with heat-resistant insulation and sealant.
Water is poured into the inner mug, and the entire structure is put on fire. In a few minutes you can check output voltage multimeter.
In order to assemble a thermoelectric generator yourself, you will need the following materials:
- Peltier element";
- a housing from an old computer power supply for making a mini-firebox;
- voltage converter with USB output to 5V with input 1-5V;
- radiator with processor cooler;
- thermal paste.
The costs here are small and the device is quite capable of charging mobile phone. The self-assembled generator is an analogue of the foreign model from BioLite. If you assemble it carefully, the device will work reliably for a long time, since there is nothing to break here. It is only important not to overheat the Peltier element, which could cause it to fail.
When using a cooler to cool a radiator, it should be connected to a generator, after which part of the generated energy will be spent on cooling.
Despite the additional energy consumption, the efficiency of the installation will increase. If the radiator gets very hot during operation, it is necessary to take measures to cool it. Otherwise, the generator's operating efficiency will be low.
The characteristics of the generator are as follows:
- output voltage – 5V;
- load power – 0.5A;
- output type – USB;
- fuel - any.
The device is manufactured as follows:
- disassemble the power supply, leaving the case;
- glue the Peltier module to the radiator with thermal paste. It is necessary to glue with the cold side where the marking is applied;
- clean and polish the outer side surface of the power supply housing and glue the element to it with the other side (together with the radiator);
- Solder the wires from the input of the voltage converter to the terminals of the plate.
You can check the TEG by placing thin branches inside the firebox and setting them on fire. After a few minutes, you can connect your phone, which requires a temperature difference of 1000C between the sides of the module to recharge. The figure below shows the assembled generator.
DIY assembled thermoelectric generator
When using TEG, it is necessary to observe the polarity of connecting the modules.
. Thermoelectric generator
The Peltier effect makes it possible to create small generators and refrigerators that operate without moving parts. Improving the quality of modules and reducing the energy consumption of mobile devices allows you to create a thermoelectric generator with your own hands to charge batteries and supply a small amount of energy various devices, where efficiency is not particularly important.
Source: https://elquanta.ru/generatory/termoehlektricheskijj-generator.html
In order to obtain electricity, you need to find a potential difference and a conductor. People have always strived to save money, and in an era of ever-increasing utility bills, this is not at all surprising.
Today there are already ways in which a person can obtain free electricity that is free for him.
As a rule, these are certain do-it-yourself installations, which are based on an electric generator.
A thermoelectric generator is a device that allows you to generate electrical energy from heat. This is an excellent steam source of electricity, although with low efficiency.
Thermoelectric generators, which use the operating principle of conventional thermocouples, are used as a device for directly converting heat into electrical energy.
Essentially, thermoelectricity is the direct conversion of heat into electricity in liquid or solid conductors, and then the reverse process of heating and cooling the contact of different conductors using an electric current.
Heat generator device:
- The thermal generator has two semiconductors, each consisting of a certain number of electrons;
- They are also interconnected by a conductor, above which there is a layer capable of conducting heat;
- A thermionic conductor is also attached to it for transmitting contacts;
- Next comes the cooling layer, followed by the semiconductor, whose contacts lead to the conductor.
Unfortunately, a heat and power generator is not always able to operate with high power, so it is used mainly in everyday life, and not in production.
Today, the thermoelectric converter is almost never used anywhere. It “requests” a lot of resources, it also takes up space, but the voltage and current that it can generate and convert are very small, which is extremely unprofitable.
Solar thermal generator of electricity and radio waves
Sources of electrical energy can be very different. Today, the production of solar thermoelectric generators has become increasingly popular. Such installations can be used in lighthouses, in space, in cars, and in other areas of life.
Solar thermal generators are a great way to save energy resources
RTG (stands for radionuclide thermoelectric generator) works by converting the energy of isotopes into electrical energy. This is a very economical way that allows you to get practically free electricity and the possibility of lighting in conditions of no electricity.
Features of RTG:
- It is easier to obtain a source of energy from the decay of isotopes than, for example, doing the same thing by heating a burner or kerosene lamp;
- The generation of electricity and the decay of particles is possible with the presence of special isotopes, because the process of their decay can last for decades.
When using such an installation, you need to understand that when working with old models of equipment, there is a risk of receiving a dose of radiation, and it is very difficult to dispose of such a device. If destroyed incorrectly, it can act as a radiation bomb.
When choosing an installation manufacturer, it is better to choose companies that have already proven themselves. Such as Global, Altec, Tgm, Kryotherm, Termiona.
By the way, another good way to get electricity for free is a generator that collects radio waves. It consists of pairs of film and electrolytic capacitors, as well as low-power diodes. An insulated cable of about 10-20 meters is used as an antenna and another grounding wire is attached to a water or gas pipe.
How to make a Peltier element with your own hands
A typical Peltier element is a plate assembled from parts of various metals, with connectors for connecting to a network. Such a plate passes current through itself, heating up on one side (for example, up to 380 degrees) and working from the cold on the other.
The Peltier element is a special thermoelectric converter that operates on the same principle of supplying electric current
This thermogenerator has the opposite principle:
- One side can be heated by burning fuel (for example, a wood fire or some other raw material);
- The other side, on the contrary, is cooled by a liquid or air heat exchanger;
- Thus, current is generated on the wires, which can be used according to your needs.
True, the device’s performance is not very high, and the effect is not impressive, but, nevertheless, such a simple homemade module can easily charge a phone or connect an LED flashlight.
This generator element has its advantages:
- Silent operation;
- The ability to use what is at hand;
- Light weight and mobile.
Such homemade stoves have begun to gain popularity among those who like to spend the night in the forest by the fire, taking advantage of the gifts of the earth and who are not averse to getting electricity for free.
The Peltier module is also used to cool computer boards: the element is connected to the board and as soon as the temperature becomes higher than permissible, it begins to cool the circuits. On one side, cold air space enters the device, and on the other, hot air. The 50X50X4mm (270w) model is popular. You can buy such a device in a store or make it yourself.
By the way, connecting a stabilizer to such an element will allow you to get an excellent output Charger for household appliances, and not just a thermal module.
To make a Peltier element at home, you need to take:
- Bimetal conductors (about 12 pieces or more);
- Two ceramic plates;
- Cables;
- Soldering iron.
The manufacturing scheme is as follows: the conductors are soldered and placed between the plates, after which they are tightly fixed. In this case, you need to remember about the wires, which will then be attached to the current converter.
The scope of use of such an element is very diverse. Since one of its sides tends to cool, using this device you can make a small camping refrigerator, or, for example, a car air conditioner.
But, like any device, this thermocouple has its pros and cons. The advantages include:
- Compact size;
- Possibility of working with cooling or heating elements together or each separately;
- Quiet, almost silent operation.
Minuses:
- The need to control temperature differences;
- High energy consumption;
- Low level of efficiency at high cost.
Simple homemade generator
Despite the fact that these devices are not popular now, this moment There is nothing more practical than a thermogenerating unit, which, when traveling, is quite capable of replacing an electric stove, a light bulb, or helping out if the charger for a mobile phone is broken, powering the electric window. Such electricity will also help at home in case of a power outage. It can be obtained for free, one might say, on a ball.
So, to make a thermoelectric generator, you need to prepare:
- Voltage regulator;
- Soldering iron;
- Any body;
- Radiators for cooling;
- Thermal paste;
- Peltier heating elements.
Device assembly:
- First, the body of the device is made, which should be without a bottom, with holes at the bottom for air and at the top with a stand for a container (although this is not necessary, since the generator may not work on water);
- Next, a Peltier element is attached to the case, and a cooling radiator is attached to its cold side through thermal paste;
- Then you need to solder the stabilizer and the Peltier module, according to their poles;
- The stabilizer should be very well insulated to prevent moisture from getting in;
- It remains to check its operation.
By the way, if it is not possible to get a radiator, you can use a computer cooler or a car generator instead. Nothing bad will happen from such a replacement.
The stabilizer can be purchased with a diode indicator that will give a light signal when the voltage reaches the specified value.
Such a heat generator warms up in about 30 seconds, but the voltage it consumes already reaches several volts. After a few minutes of warming up, the generator will be ready for use.
Do-it-yourself thermocouple: process features
What is a thermocouple? A thermocouple is an electrical circuit consisting of two different elements with an electrical contact.
The thermoEMF of a thermocouple with a temperature difference of 100 degrees at its edges is approximately 1 mV. To make it higher, several thermocouples can be connected in series. The result is a thermopile, the thermoEMF of which will be equal to the total sum of the EMF of the thermocouples included in it.
The thermocouple manufacturing process is as follows:
- A strong connection is created between the two different materials;
- Take a voltage source (for example, car battery) and wires of different materials pre-twisted into a bundle are connected to one end;
- At this time, you need to bring a lead connected to graphite to the other end (a regular pencil lead will do here).
By the way, for safety it is very important not to work under high voltage! The maximum indicator in this regard is 40-50 Volts. But it is better to start with small powers from 3 to 5 kW, gradually increasing them.
There is also a “water” way to create a thermocouple. It consists in ensuring the heating of the connected wires of the future structure by an arc discharge that appears between them and a strong solution of water and salt.
During this interaction, “water” vapors bind the materials together, after which the thermocouple can be considered ready. In this case, it matters what diameter the product harness is.
It shouldn't be too big.
Free electricity with your own hands (video)
Getting free electricity is not as difficult as it seems. Thanks to various types of generators that work with different sources, it is no longer scary to be left without light during a power outage. A little skill and you already have your own mini-station for generating electricity.
Source: http://6watt.ru/elektrosnabzhenie/besplatnoe-elektrichestvo
Peltier module: technical characteristics
The thermal converter (Peltier module) operates on the reverse principle of the thermocouple - the appearance of a temperature difference when electric current flows.
How does the Peltier element work?
It is quite simple to use a Peltier module, the principle of which is to release or absorb heat at the moment of contact between different materials when current passes through it. The energy flux density of electrons before and after contact is different.
If it is less at the outlet, it means heat is generated there. When electrons in contact are inhibited by an electric field, they transfer kinetic energy to the crystal lattice, heating it up. If they accelerate, heat is absorbed.
This occurs due to the fact that part of the energy is taken from the crystal lattice and it cools.
To a large extent, this phenomenon is inherent in semiconductors, which is explained by the large difference in charges.
The Peltier module, the application of which is the topic of our review, is used in the creation of thermoelectric cooling devices (TECs). The simplest of them consists of two p- and n-type semiconductors connected in series through copper contacts.
If electrons move from a semiconductor "p" to "n", at the first junction with a metal bridge they recombine, releasing energy.
The next transition from the semiconductor “p” to the copper conductor is accompanied by the “pulling” of electrons through the contact by an electric field.
This process leads to energy absorption and cooling of the area around the contact. Processes occur in a similar way at the following transitions.
By placing heated and cooled contacts in different parallel planes, a practical implementation of the method will be obtained. Semiconductors are made from selenium, bismuth, antimony or tellurium. The Peltier module houses a large number of thermocouples placed between aluminum nitride or aluminum oxide ceramic plates.
Factors influencing the efficiency of TEM
- Current strength.
- Number of thermocouples (up to several hundred).
- Types of semiconductors.
- Cooling rate.
Larger values have not yet been achieved due to low efficiency (5-8%) and high cost. For a TEM to work successfully, it is necessary to ensure effective heat removal from the heated side.
This creates difficulties in the practical implementation of the method. If the polarity is reversed, the cold and hot sides reverse each other.
Advantages and disadvantages of modules
The need for TEMs arose with the advent of electronic devices requiring miniature cooling systems. The advantages of the modules are as follows:
- compactness;
- no moving joints;
- the Peltier module has a reversible operating principle when changing polarity;
- simplicity of cascade connections for increased power.
The main disadvantage of the module is low efficiency. This manifests itself in high power consumption to achieve the required cooling effect. In addition, it has a high cost.
Application of TEM
The Peltier module is used primarily for cooling microcircuits and small parts. A start was made for cooling elements of military equipment:
- microcircuits;
- infrared detectors;
- laser elements;
- crystal oscillators.
The Peltier thermoelectric module has gradually become used in household appliances: for creating refrigerators, air conditioners, generators, thermostats. Its main purpose is to cool small objects.
CPU cooling
The main components of computers are constantly being improved, which leads to an increase in heat generation. Together with them, cooling systems are developing using innovative technologies, with modern means control.
The Peltier module has found application in this area primarily in cooling microcircuits and other radio components. Traditional coolers can no longer cope with forced overclocking modes of microprocessors.
And increasing the frequency of processors makes it possible to increase their performance.
Increasing the fan speed results in significant noise. It is eliminated by using a Peltier module in a combined cooling system. In this way, leading companies quickly mastered the production of efficient cooling systems, which began to be in great demand.
Heat is usually removed from processors by coolers. The air flow can be sucked in from outside or come from inside the system unit. the problem is that the air temperature is sometimes insufficient for heat removal.
Therefore, TEMs began to be used to cool the air flow entering the system unit, thereby increasing the efficiency of heat transfer.
Thus, the built-in air conditioner is an assistant to the traditional computer cooling system.
Aluminum radiators are attached to both sides of the module. From the cold plate side, cooling air is pumped into the processor. After it takes the heat, another fan blows it out through the module's hot plate heatsink.
A modern TEM is controlled by an electronic device with a temperature sensor, where the degree of cooling is proportional to the heating of the processor.
Activating processor cooling also creates some problems.
- Simple Peltier cooling modules are designed for continuous operation. Lower power consumption also reduces heat dissipation, which can cause the chip to overcool and subsequently freeze the processor.
- If the operation of the cooler and refrigerator are not properly coordinated, the latter may switch to heating mode instead of cooling. The additional heat source will cause the processor to overheat.
Thus, modern processors require advanced cooling technologies that control the operation of the modules themselves. Such changes in operating modes do not occur with video cards, which also require intensive cooling. Therefore, TEM is ideal for them.
Do-it-yourself car refrigerator
In the middle of the last century, the domestic industry tried to master the production of small-sized refrigerators based on the Peltier effect. Existing technologies of that time did not allow this to be done. Nowadays the limiting factor is mainly high price, but attempts continue, and success has already been achieved.
Widespread production of thermoelectric devices allows you to create a small refrigerator with your own hands, convenient for use in cars. Its basis is a “sandwich”, which is made as follows.
- A layer of heat-conducting paste type KPT-8 is applied to the upper radiator and the Peltier module is glued to one side of the ceramic surface.
- Similarly, another radiator is attached to it from the bottom side, intended for placement in the refrigerator chamber.
- The entire device is tightly compressed and dried for 4-5 hours.
- Coolers are installed on both radiators: the upper one will remove heat, and the lower one will equalize the temperature in the refrigerator chamber.
The refrigerator body is made with a heat-insulating gasket inside. It is important that it closes tightly. You can use a regular plastic tool box for this.
12V power is supplied from the vehicle system. It can also be made from a 220 V AC network, with a power supply. The simplest AC to DC conversion circuit is used.
It contains a rectifier bridge and a ripple-smoothing capacitor. It is important that at the output they do not exceed 5% of the nominal value, otherwise the efficiency of the device is reduced. The module has two outputs made of colored wires.
“Plus” is always connected to red, and “minus” to black.
The power of the TEM must correspond to the volume of the box. The first 3 digits of the marking indicate the number of pairs of semiconductor microelements inside the module (49-127 or more). The current strength is expressed by the last two digits of the marking (from 3 to 15 A). If the power is not enough, you need to glue another module onto the radiators.
Note! If the current exceeds the power of the element, it will heat up on both sides and quickly fail.
Peltier module: electrical energy generator
TEM can be used to generate electricity. To do this, it is necessary to create a temperature difference between the plates, and the thermocouples located between them will generate electric current.
For practical use you need a TEM with at least 5 V. Then you can use it to charge your mobile phone. Due to the low efficiency of the Peltier module, a DC-DC boost converter will be required. To assemble the generator you will need:
- 2 Peltier modules TEC1-12705 with plate size 40x40 mm;
- converter EK-1674;
- aluminum plates 3 mm thick;
- water pan;
- heat resistant glue.
Two modules are placed between the plates with glue, and then the entire structure is fixed to the bottom of the pan. If you fill it with water and put it on fire, you get the required temperature difference, which produces an EMF of the order of 1.5 V. By connecting the modules to a boost converter, you can increase the voltage to 5 V, which is necessary to charge the phone battery.
The greater the temperature difference between the water and the lower heated plate, the more efficient the generator is. Therefore, we must try to reduce the heating of the water different ways: make it flow-through, replace it with fresh one more often, etc.
An effective means of increasing the temperature difference is the cascade switching of modules, when they are layered one on top of the other.
Increasing the overall dimensions of the device allows you to place more elements between the plates and thereby increase the overall power.
The generator's performance will be sufficient to charge small batteries, operate LED lamps or radio. Note! To create thermal generators, you will need modules capable of operating at 300-400 0C! The rest are only suitable for trial testing.
Unlike other means of alternative generation of electricity, they can work while driving if you create something like a catalytic heater.
Domestic Peltier modules
TEMs of their own production appeared on our market not so long ago. They are highly reliable and have good characteristics. The Peltier module, which is in wide demand, has dimensions of 40x40 mm. It is designed for a maximum current of 6 A and voltage up to 15 V.
A domestic Peltier module can be purchased for a low price. With a power consumption of 85 W, it creates a temperature difference of 60 0C. Together with the cooler, it is capable of protecting the processor from overheating with a power dissipation of 40 W.
Characteristics of modules from leading companies
Foreign devices are presented on the market in greater variety. To protect processors from leading companies, a PAX56B Peltier module is used as a refrigerator, the price of which, complete with a fan, is $35.
With dimensions of 30x30 mm, it maintains the processor temperature no higher than 63 0C with a power output of 25 W. For power supply, a voltage of 5 V is sufficient, and the current does not exceed 1.5 A.
The PA6EXB Peltier module is well suited for cooling the processor, providing normal temperature conditions with a dissipation power of 40 W. The area of its module is 40x40 mm, and the current consumption is up to 8 A. In addition to its impressive dimensions - 60x60x52.5 mm (including the fan) - the device requires free space around it. Its price is $65.
When the Peltier module is used, specifications it must meet the needs of the cooled devices. It is unacceptable that their temperature is too low. This can lead to moisture condensation, which can be harmful to electronics.
Modules for the manufacture of generators, such as TEC1-12706, TEC1-12709, are distinguished by higher power - 72 W and 108 W, respectively. They are distinguished by markings, which are always applied to the hot side.
The maximum permissible temperature of the hot side is 150-160 0C. The greater the temperature difference between the plates, the higher the output voltage.
The device operates at a maximum temperature difference of 600 0C.
You can buy a Peltier module inexpensively - about $10 or less per piece, if you look hard enough. Quite often, sellers significantly inflate their prices, but you can find them several times cheaper if you buy them on sale.
Conclusion
The Peltier effect has now found application in the creation of small refrigerators necessary modern technology. The reversibility of the process makes it possible to produce micropower plants that are in demand for charging batteries of electronic devices.
Unlike other means of alternative power generation, they can operate while driving if a catalytic heater is installed.
A huge number of electronic devices absorb electrical energy, which must be constantly renewed. While on the road, you have to carry chemical current sources with you or generate electricity from mechanical energy using complex and bulky devices.
Type of thermoelectric generator
Even earlier, Seebeck discovered the occurrence of thermo-EMF in a circuit of dissimilar conductors when maintaining different temperatures at the point of contact. Based on thermoelectric effects, a so-called Peltier element or module was created, which consists of 2 ceramic plates with a bimetal located between them. When electric current is applied through them, one side of the plate heats up and the other cools, which makes it possible to create refrigerators from them. The figure below shows modules of different sizes used in technology.

Peltier modules of different sizes
The process is reversible: if you maintain a temperature difference across the elements on both sides, they will generate an electric current, which allows the device to be used as a thermoelectric generator to generate a small amount of electricity.
The Peltier effect is the release of heat at the point of contact of dissimilar conductors when electric current flows through them.
Operating principle of modules
At the contact of dissimilar conductors, heat is released or absorbed depending on the direction of the electric current. The flow of electrons has potential and kinetic energy. The current density in the contacting conductors is the same, but the energy flux densities are different.
If the energy flowing into the contact is greater than the energy flowing out of it, this means that electrons are slowed down at the point of transition from one region to another and heat up the crystal lattice (the electric field slows down their movement). When the direction of the current changes, the reverse process of electron acceleration occurs, when energy is taken from the crystal lattice and its cooling occurs (the directions of the electric field and the movement of electrons coincide).
The energy difference of charges at the boundary of semiconductors is the highest and the effect manifests itself most strongly there.
Peltier module
The most common is the thermoelectric module (TEM), which is p- and n-type semiconductors connected to each other through copper conductors.

Diagram of the operating principle of the module
In one element there are 4 transitions between metal and semiconductors. In a closed circuit, the flow of electrons moves from the negative pole of the battery to the positive, sequentially passing through each transition.
Near the first copper-p-type semiconductor transition, heat is released in the semiconductor zone as electrons move to a state with lower energy.
Near the next boundary with the metal in the semiconductor, heat is absorbed due to the “sucking out” of electrons from the p-conductivity zone under the influence of an electric field.
In the third transition, electrons enter the n-type semiconductor, where they have higher energy than in the metal. In this case, energy is absorbed and the semiconductor is cooled near the transition boundary.
The last transition is accompanied by a reverse process of heat release in the n-semiconductor due to the transition of electrons to a zone with lower energy.
Since the heating and cooling transitions are in different planes, the Peltier element will be cooled from above and heated from below.
In practice, each element contains a large number of heating and cooling transitions, which leads to the formation of a noticeable temperature difference, which makes it possible to create a thermoelectric generator.

What does the module structure look like?
The Peltier element contains a large number of p- and n-type semiconductor parallelepipeds, connected in series with metal jumpers - thermal contacts, the other side in contact with the ceramic plate.
Bismuth telluride and silicon germanide are used as semiconductors.
Advantages and disadvantages of TEM
The advantages of a thermoelectric module (TEM) include:
- small sizes;
- the ability to operate both coolers and heaters;
- reversibility of the process when changing polarity, allowing you to maintain an exact temperature value;
- absence of moving elements that usually wear out.
Disadvantages of modules:
- low efficiency (2-3%);
- the need to create a source that provides a temperature difference;
- significant energy consumption;
- high price.
Despite the disadvantages, TEMs are used where large energy costs are not important:
- cooling of chips, parts of digital cameras, diode lasers, quartz oscillators, infrared detectors;
- the use of TEM cascades to achieve low temperatures;
- creation of compact refrigerators, for example, for cars;
- thermoelectric generator for charging mobile devices.
With low productivity, it is advisable to use TEGs in camping conditions, where it is necessary to obtain electricity to charge a cell phone or LED light bulb. The simplicity of the design allows you to make an electric generator with your own hands.
Alternative sources also include solar panels or a wind generator. The former require special conditions - the presence of sunlight, which may not always be available. Another source is large and requires wind. Another disadvantage is the presence of moving parts that reduce reliability and are heavy.
Industrial thermogenerators
BioLite has developed a new model for hiking that allows you to cook food in a compact, portable wood-burning stove and at the same time charge your mobile device from the built-in TEG.

Compact portable wood stove
The device will come in handy everywhere: fishing, hiking, at the dacha. Anything that burns can be used as fuel.
When fuel is burned in the furnace, heat is transferred through the wall to the module, which generates electricity. At a voltage of 5V, the output power is 2-4 W, which is enough to charge many types of mobile devices and operate LED lighting. The red arrow shows the direction of movement of heat, the blue arrow shows cold air into the furnace, the yellow arrow shows the supply of electricity to rotate the air intake fan and to the generator output via USB.

Scheme of operation of BioLite TEG on wood
The Indigirka generator furnace, developed by the St. Petersburg company Kryotherm, has the following characteristics:
- thermal power – 6 kW;
- weight – 56 kg;
- dimensions – 500x530x650 mm;
- email power at voltage 5V – 60 W.
The stove is a conventional heating and cooking stove, with thermoelectric generators attached on both sides.

What does the thermoelectric generator furnace "Indigirka" look like?
The device is quite convenient, but the price is impressive - 50 thousand rubles. Although the stove is intended for camping conditions, it will clearly not be affordable for ordinary hunters and fishermen. As a heating system, it is no better than conventional and cheaper models.
If you attach a TEG to a simple stove, the homemade device will work perfectly.
DIY TEG
To assemble a thermoelectric generator with your own hands, you need the following elements:
- Module. To generate electric current, not all modules can be used, but only those that can withstand heating up to 300-400 0 C. Having a heating reserve is necessary, since even with slight overheating the element fails. The most common models are the TEC1-12712 type in the form of square plates with a side size of 40, 50 or 60 mm.
If you take the maximum size, it is enough to use one element in a DIY design. The first 3 digits of the marking - 127 - mean how many elements are contained in 1 plate. The last numbers show the maximum permissible current, which is 12 A.
- Boost converter. It is necessary to obtain a constant voltage of 5V. The generator may produce less voltage, which needs to be increased. The devices are produced foreign (types 5V NCP1402 and MAX 756) and domestic (3.3V/5V EK-1674). To charge your mobile phone, you should choose a device with a USB connector.
- Heater. The simplest options are a fire, a candle, a homemade lamp or a miniature stove.
- Cooler. The easiest way is to use water or, in winter, snow.
- Connecting elements. Equipment is needed to create the maximum possible temperature difference between the two sides of the plate. Here the choice is up to the craftsmen; they most often use 2 mugs or pans of different sizes, the handles of which are sawed off and where one is inserted inside the other. A module is placed between them and secured with thermal paste. 2 wires are soldered to it and connected to a voltage converter.
To increase the efficiency of the generator, the bottoms of the metal surfaces of mugs or pans in contact with the generator plate should be polished. In addition, heat-resistant sealant is applied to the spaces between the bottoms of the smaller and larger mugs. Then the heat from heating will be localized at the location of the module.
The wires between the module and the converter are protected with heat-resistant insulation and sealant.
Water is poured into the inner mug, and the entire structure is put on fire. After a few minutes, you can check the output voltage with a multimeter.
In order to assemble a thermoelectric generator yourself, you will need the following materials:
- Peltier element";
- a housing from an old computer power supply for making a mini-firebox;
- voltage converter with USB output to 5V with input 1-5V;
- radiator with processor cooler;
- thermal paste.
The costs here are small and the device is quite capable of charging a mobile phone. The self-assembled generator is an analogue of the foreign model from BioLite. If you assemble it carefully, the device will work reliably for a long time, since there is nothing to break here. It is only important not to overheat the Peltier element, which could cause it to fail.
When using a cooler to cool a radiator, it should be connected to a generator, after which part of the generated energy will be spent on cooling.
Despite the additional energy consumption, the efficiency of the installation will increase. If the radiator gets very hot during operation, it is necessary to take measures to cool it. Otherwise, the generator's operating efficiency will be low.
The characteristics of the generator are as follows:
- output voltage – 5V;
- load power – 0.5A;
- output type – USB;
- fuel - any.
The device is manufactured as follows:
- disassemble the power supply, leaving the case;
- glue the Peltier module to the radiator with thermal paste. It is necessary to glue with the cold side where the marking is applied;
- clean and polish the outer side surface of the power supply housing and glue the element to it with the other side (together with the radiator);
- Solder the wires from the input of the voltage converter to the terminals of the plate.
You can check the TEG by placing thin branches inside the firebox and setting them on fire. After a few minutes, you can connect your phone, which requires a temperature difference of 100 0 C between the sides of the module to recharge. The figure below shows the assembled generator.

DIY assembled thermoelectric generator
When using TEG, it is necessary to observe the polarity of connecting the modules.
Video. Thermoelectric generator
The Peltier effect makes it possible to create small generators and refrigerators that operate without moving parts. Improving the quality of modules and reducing the energy consumption of mobile devices allows you to create a thermoelectric generator with your own hands to charge batteries and supply a small amount of energy to various devices where efficiency is not particularly important.
The best time to operate a thermogenerator based on Peltier elements is, of course, winter. Because they need to be well cooled to get anything at all.
In the experiment testing a powerful generator, 12 TEC1-12706 Peltier modules were used. The cheapest and most popular are sold in this Chinese store. There is a cooling cooler for it.
Cooling in the example shown was provided by a 5.4 watt, 12 volt fan.
What a Peltier element is, what its characteristics are, how it works, and the design of working models, is described in several articles on our website, which you can easily find through the convenient search bar.
The purpose of the experiment is to find out what maximum power the cheapest Chinese thermocouple can produce in the winter season.
So, with the beginning of the experiment, the stove was lit, when the wood flared up a little, the thermogenerator began to work and the fan started. It cools the cold side of the thermocouples. The scheme is simple. At the end of the video it is shown how such a thermogenerator is assembled.
During the experiment, the maximum open circuit voltage of this generator will be achieved. Then, using a potentiometer, this voltage will be reduced by exactly half. This levels the generator resistance and load resistance. Then the same amount of power is dissipated in the generator and in the load. This will give 50 percent power, or rather an efficiency of 50% of the delivered power. This corresponds to an efficiency of only 50%. But the output of such power will be maximum in this ratio. But maximum power transmission occurs only with this ratio!
As the furnace heats up, the voltage produced by the electric generator increases. The fan has picked up speed, it is a fairly powerful fan with a power of 5.5 watts. Therefore, it will take part of the power to itself. The power that will now be determined will be useful power. The voltage does not rise above 26 volts. We connect the potentiometer and start adding resistance.
Now we smoothly increase the voltage to 13 volts. The power recorded was 9 watts. While the settings were being made, the generator warmed up and the power dropped by 1.5 watts.
We were able to get up to 9 watts for a short time. But then the power dropped and stopped at around 7.5 watts. But this figure remained stable. This power is enough to charge any phone, smartphone or tablet.
From 12 Peltier elements, 0.5 watts or more per element is obtained. At an air temperature of zero degrees, this is a good indicator for air cooling. At a temperature of -20, the result would be an order of magnitude higher. Therefore, it is quite possible to get even up to one watt per Peltier element, but in extreme cold.
Now the fan will be connected through a wattmeter in order to see how much useful energy is spent on its operation. The device showed 6 watts. If it were not for this fan, it would be possible to add another 5-6 watts to the power of this thermal generator.
To continue the experiment, it was planned to turn off the fan so that cooling could be done using snow. After the fan is reset, the radiator will be heavily covered with snow. However, an unexpected accident occurred in the experiment. After the fan was removed, the stove overheated and one of the Peltier elements failed, melting without cooling. The system has lost contacts. Therefore the fan is in this device useful element. For safety, it is necessary to use protective grilles.
The conclusion is as follows: about 1 watt per Peltier element can be obtained in good frost. There are places, for example Yakutia or the far north, where temperatures reach minus 50 degrees Celsius. So it will be easy to get 1 watt from an element. Imagine there is a stove in a yurt, and behind it there is a wall measuring 1 x 2 m. The warm side is inside the stove, and the cold side is outside, where there is frost and wind. From one square meter of such elements you can remove up to 0.5 kilowatts of electricity. That is, from 2 square meters you can get up to one kilowatt of electricity.
Such powerful furnaces based on elements are produced in Russia. They are called “Electric generating furnace Indigirka”. You can buy them in this store, discount code 11920924.
The design of such a thermogenerator is extremely simple. 12 of the cheapest Chinese Peltier elements are clamped between two aluminum radiators, which should have smooth, ideally polished, surfaces. Naturally, thermal paste is applied to each side of the thermoelement. We twist the radiators with bolts and connect them with wires. We attach the cooler, preferably a more powerful one. Well, the stove itself. This is a piece of galvanized steel, better than stainless steel. Attaches to the hot radiator with bolts. Then a bottom is made with 7-8 mm holes for air intake.
There is a continuation of this experiment. To find it, write in the site search: Air-cooled Peltier.
In this final article, I will tell you that these modules are not only capable of providing a temperature difference on their sides with a decent amount of electricity, but they are also capable of generating electricity if one side of the element is forcibly cooled and the other heated.
No load, temperature difference ~100°C
In these tests, a small module TB109-0.6-0.8 volunteered, with a surface area of only 3.12 sq. cm. Let me remind you of its role.., appearance and characteristics:
To test Peltier in electric generator mode, a small stand was assembled, which contains the following devices: a heater, a voltmeter, an ammeter and a load, a radiator and a piece of ice in a waterproof bag were also needed, and of course the experimental TB109-0.6-0.8 itself. The heater was a 20W 5.6 Ohm resistor, which was heated to about 80-90 degrees. To improve the thermal contact of the Peltier element with the heater, a Namaconda thermal conductive gasket was used, pulled out from some worn-out computer unit nutrition.
Let's start testing.
The first test was carried out with a 1 Ohm load connected to the Peltier pins, and a room temperature radiator was used as a cooler.
We managed to get 0.117V from the module at a current of 119.5mA or 14mW, with a temperature difference of approximately 60 degrees.
Load 1 Ohm, temperature difference ~100°C
With a temperature difference of 100 degrees, the module produced better results, namely: 0.21V 0.22A or 46mW.
The following test was carried out with a load of 20 ohms.
Load 20 Ohm, temperature difference ~100°C
The module produced 1.31V at a current of 66mA or 86mW.
At idle, first photo, the module produced 2.19V.
Conclusion - Peltier modules can be successfully used to generate electricity. If the module contains 109 thermocouples, with an area of 3.12 sq.cm. with a temperature difference of 100 degrees, it was able to produce 86 mW at one and a half volts and more than 2 V at idle, then a module with a much larger area and temperature difference is enough to power a small LED illuminator or radio, or to charge batteries. But, unfortunately, their use is greatly limited by their price.
Examples of application: various TAGs, from portable tourist ones, which can be attached to a pot by the fire and listen to the radio, to RTGs, which are used to power remote, hard-to-reach autonomous objects (for example, lighthouses) or on space satellites.
Gratitude for the modules provided to the company – Radioelectronics.
When purchasing in the amount of 3000 rubles.
Shop "World of Solar Energy"Solbat Company offers:
4.8V 669 mA - module on the Seebeck effectfor generating electricity, maximum power 3.4 watts, maximum voltage 4.8 volts, maximum current 669 mA, Peltier-Seebeck thermal generator of electrical energy.
==============================================================
CharacteristicsT(white - white) :
- Maximum voltage: DC 4.8V
- Maximum current: 669mA
- Maximum performance: 3.4W
- Module type: single-stage
- Operating temperature: 150?
- Module dimensions: 40 x 40 x 4mm
==============================================================
Reference
Peltier element
The Peltier element is a thermoelectric converter, the operating principle of which is based on the Peltier effect - the occurrence of a temperature difference when an electric current flows. In English-language literature, Peltier elements are designated TEC (from the English Thermoelectric Cooler - thermoelectric cooler). The opposite effect of the Peltier effect is called the Seebeck effect.
Thermal generator module based on the Seebeck effect
The Seebeck effect is the phenomenon of the occurrence of EMF in a closed circuit. electrical circuit, consisting of series-connected dissimilar conductors, the contacts between which are at different temperatures. The Seebeck effect is also sometimes simply called the thermoelectric effect.
Peltier-Seebeck thermoelement as a thermoelectric generator.
To generate electricity, you need to cool one side of the thermoelement and heat the other. When there is a temperature difference between the cold and hot sides of the thermoelement, a difference in electrical potential occurs - + and - appear. The greater the difference between these temperatures, the higher the power of the thermoelectric generator.
To increase the output voltage from the thermocouple, it can be connected to.
The Peltier-Seebeck thermoelement is like a refrigerator - a heater.
To obtain heat or cold, you need to connect a source of electricity to the terminals of the thermoelement:
When electric current flows through the thermoelement, one side will heat up, the other side will cool down to sub-zero temperatures. The greater the current, the higher the difference between these temperatures, of course within certain limits. When changing the polarity of the supply voltage, the hot and cold sides also change places.
==============================================================
Description tthermoelectric generator SP1848-27145
representsceramic flat platewith dimensions 40 by 40 and thickness 4 mm.
Between ceramic plates thermogenerator SP1848series-connected semiconductor elements of n and p types are located.
Module housing thermogenerator SP1848sealed, the ceramic surface is polished, however, the use of heat-conducting paste is mandatory.Black (-) and red (+) wires are soldered to the thermocouple terminals.
Module t used for do-it-yourself assembly at home of both stationary and mobile electrical energy generators
Mobile element to generate electricity SP1848, allows you to charge the battery of a mobile device in emergency situations when there is no access to an electrical outlet.
Advantage of thermoelectric modules:
- works always and wherever there is heat and cold
- noiselessness, high reliability and durability
- absence of vibrations and moving, wearing parts
- Possibility of cascade connection - serial, parallel, in groups
A detailed description and operating principle of thermoelectric modules based on Peltier elements can be found in.
Thermoelectric generators will help you save your costs on burned fuel!
By heating a room with a hot water boiler, you can get additional electricity almost free of charge!
Light weight, small size, easy to use, makes T thermogeneratorSP1848-27145irreplaceable and versatile in extreme situations.
==============================================================
ApplicationTthermoelectric generator SP1848-27145
As a rule, Peltier elements are used mainly as cold generators when designing mobile refrigerators, mini bars, and coolers for soft drinks.
Seebeck modules are used specifically for generating electricity, that is, as thermoelectric generators. This is the main difference between Seebeck thermal generators and Peltier modules.
If one side of a thermoelectric generator is heated and the other side is cooled, the element begins to generate electricity.
All that is needed for a thermogenerator to operate is a source of heat and cold.
You can use the sun, hot water, a candle or a fire as a heat source. The thermoelectric generator can be cooled with cold water, ice, snow or cold wind.
The scope of application of the heat generator is practically unlimited.
Thermal electric generators Irokos are used in conjunction with gas boilers and stoves, geothermal springs, cooking stoves, hot water and heating systems, and just ordinary fires.
Having an indispensable and versatile compact T thermoelectric generator , you can charge your phone, smartphone, tablet, player, camera or any other mobile device at any time and anywhere.
Using tthermoelectric generator SP1848 You can generate electricity while hiking, traveling, or expeditions to provide power, lighting, and charging various devices.
Thermoelectric generator SP1848, indispensable for tourists - by lighting a fire to warm up or cook food, you can recharge the batteries of mobile devices and LED flashlights!